
new Mayo Clinic study found that 40% of pancreatic cancer patients are diagnosed with diabetes prior to their pancreatic cancer diagnosis

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


new Mayo Clinic study found that 40% of pancreatic cancer patients are diagnosed with diabetes prior to their pancreatic cancer diagnosis

US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted priority review for bortezomib (Velcade) in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma

Gastrointestinal stromal tumors have until recently had a uniformly poor prognosis with lack of effective drug therapies. These tumors usually have activating mutations in either KIT or PDGFR-α tyrosine kinase receptors. Over the past decade, imatinib (Gleevec), a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor has become the standard of care for the first-line treatment of patients with unresectable and metastatic disease. For patients with imatinib-resistant disease or intolerant to the side effects of imatinib, sunitinib (Sutent), a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor was recently approved. For earlier-stage disease, status post–complete surgical excision, preliminary data seem encouraging for the role of adjuvant imatinib in prolonging patients' disease-free interval. The impact of neoadjuvant drug therapy needs to be further classified and explored. With additional evaluation of other tyrosine kinase inhibitors and novel therapies against other molecular markers, the treatment paradigm for this malignancy should continue to evolve.

The use of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) as a method for ablation of a localized tumor growth is not new. Several attempts have been made to apply the principles of HIFU to the treatment of pelvic, brain, and gastrointestinal tumors. However, only in the past decade has our understanding of the basic principles of HIFU allowed us to further exploit its application as a radical and truly noninvasive, intent-to-treat, ablative method for treating organ-confined prostate cancer. Prostate cancer remains an elusive disease, with many questions surrounding its natural history and the selection of appropriate patients for treatment yet to be answered. HIFU may play a crucial role in our search for an efficacious and safe primary treatment for localized prostate cancer. Its noninvasive and unlimited repeatability potential is appealing and unique; however, long-term results from controlled studies are needed before we embrace this new technology. Furthermore, a better understanding of HIFU's clinical limitations is vital before this treatment modality can be recommended to patients who are not involved in well-designed clinical studies. This review summarizes current knowledge about the basic principles of HIFU and its reported efficacy and morbidity in clinical series published since 2000.

blood-based marker called colon cancer–specific antigen-2 (CCSA-2) may be an accurate indicator of colorectal cancer

The use of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) as a method for ablation of a localized tumor growth is not new. Several attempts have been made to apply the principles of HIFU to the treatment of pelvic, brain, and gastrointestinal tumors. However, only in the past decade has our understanding of the basic principles of HIFU allowed us to further exploit its application as a radical and truly noninvasive, intent-to-treat, ablative method for treating organ-confined prostate cancer. Prostate cancer remains an elusive disease, with many questions surrounding its natural history and the selection of appropriate patients for treatment yet to be answered. HIFU may play a crucial role in our search for an efficacious and safe primary treatment for localized prostate cancer. Its noninvasive and unlimited repeatability potential is appealing and unique; however, long-term results from controlled studies are needed before we embrace this new technology. Furthermore, a better understanding of HIFU's clinical limitations is vital before this treatment modality can be recommended to patients who are not involved in well-designed clinical studies. This review summarizes current knowledge about the basic principles of HIFU and its reported efficacy and morbidity in clinical series published since 2000.

US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted Cephalon's supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) for fentanyl buccal tablets (Fentora) for the management of breakthrough pain in opioid-tolerant patients with chronic pain.

Pain in older cancer patients is a common event, and many times it is undertreated. Barriers to cancer pain management in the elderly include concerns about the use of medications, the atypical manifestations of pain in the elderly, and side effects related to opioid and other analgesic drugs. The care of older cancer patients experiencing pain involves a comprehensive assessment, which includes evaluation for conditions that may exacerbate or be exacerbated by pain, affecting its expression, such as emotional and spiritual distress, disability, and comorbid conditions. It is important to use appropriate tools to evaluate pain and other symptoms that can be related to it. Pain in older cancer patients should be managed in an interdisciplinary environment using pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions whose main goals are decreasing suffering and improving quality of life. In this two-part article, the authors present a review of the management of pain in older cancer patients, emphasizing the roles of adequate assessment and a multidisciplinary team approach.

US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted the peginterferon alfa-2b (PEG-Intron) supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) for for review and has granted Priority Review status to the drug for the adjuvant treatment of patients with stage III melanoma

The use of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) as a method for ablation of a localized tumor growth is not new. Several attempts have been made to apply the principles of HIFU to the treatment of pelvic, brain, and gastrointestinal tumors. However, only in the past decade has our understanding of the basic principles of HIFU allowed us to further exploit its application as a radical and truly noninvasive, intent-to-treat, ablative method for treating organ-confined prostate cancer. Prostate cancer remains an elusive disease, with many questions surrounding its natural history and the selection of appropriate patients for treatment yet to be answered. HIFU may play a crucial role in our search for an efficacious and safe primary treatment for localized prostate cancer. Its noninvasive and unlimited repeatability potential is appealing and unique; however, long-term results from controlled studies are needed before we embrace this new technology. Furthermore, a better understanding of HIFU's clinical limitations is vital before this treatment modality can be recommended to patients who are not involved in well-designed clinical studies. This review summarizes current knowledge about the basic principles of HIFU and its reported efficacy and morbidity in clinical series published since 2000.

The use of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) as a method for ablation of a localized tumor growth is not new. Several attempts have been made to apply the principles of HIFU to the treatment of pelvic, brain, and gastrointestinal tumors. However, only in the past decade has our understanding of the basic principles of HIFU allowed us to further exploit its application as a radical and truly noninvasive, intent-to-treat, ablative method for treating organ-confined prostate cancer. Prostate cancer remains an elusive disease, with many questions surrounding its natural history and the selection of appropriate patients for treatment yet to be answered. HIFU may play a crucial role in our search for an efficacious and safe primary treatment for localized prostate cancer. Its noninvasive and unlimited repeatability potential is appealing and unique; however, long-term results from controlled studies are needed before we embrace this new technology. Furthermore, a better understanding of HIFU's clinical limitations is vital before this treatment modality can be recommended to patients who are not involved in well-designed clinical studies. This review summarizes current knowledge about the basic principles of HIFU and its reported efficacy and morbidity in clinical series published since 2000.

Despite the high prevalence of brain metastases in patients with metastatic lung cancer, these patients have been excluded from enrollment in clinical trials of new therapeutic drugs. The reasons for exclusion have centered on concerns that the blood-brain barrier may impede drug delivery into brain metastases, that brain metastases confer a dismal survival for metastatic lung cancer patients, and that brain metastases carry risk for cerebrovascular hemorrhage. A focused, updated review of these issues, however, clearly shows that these particular concerns are unwarranted. An extensive review of clinical trials on the efficacy of chemotheraputic agents against lung cancer brain metastases is also provided. This collective information describes an area in need of therapeutic development and supports an initiative to evaluate novel targeted therapies for lung cancer brain metastases.

The use of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) as a method for ablation of a localized tumor growth is not new. Several attempts have been made to apply the principles of HIFU to the treatment of pelvic, brain, and gastrointestinal tumors. However, only in the past decade has our understanding of the basic principles of HIFU allowed us to further exploit its application as a radical and truly noninvasive, intent-to-treat, ablative method for treating organ-confined prostate cancer. Prostate cancer remains an elusive disease, with many questions surrounding its natural history and the selection of appropriate patients for treatment yet to be answered. HIFU may play a crucial role in our search for an efficacious and safe primary treatment for localized prostate cancer. Its noninvasive and unlimited repeatability potential is appealing and unique; however, long-term results from controlled studies are needed before we embrace this new technology. Furthermore, a better understanding of HIFU's clinical limitations is vital before this treatment modality can be recommended to patients who are not involved in well-designed clinical studies. This review summarizes current knowledge about the basic principles of HIFU and its reported efficacy and morbidity in clinical series published since 2000.

Pain in older cancer patients is a common event, and many times it is undertreated. Barriers to cancer pain management in the elderly include concerns about the use of medications, the atypical manifestations of pain in the elderly, and side effects related to opioid and other analgesic drugs. The care of older cancer patients experiencing pain involves a comprehensive assessment, which includes evaluation for conditions that may exacerbate or be exacerbated by pain, affecting its expression, such as emotional and spiritual distress, disability, and comorbid conditions. It is important to use appropriate tools to evaluate pain and other symptoms that can be related to it. Pain in older cancer patients should be managed in an interdisciplinary environment using pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions whose main goals are decreasing suffering and improving quality of life. In this two-part article, the authors present a review of the management of pain in older cancer patients, emphasizing the roles of adequate assessment and a multidisciplinary team approach.
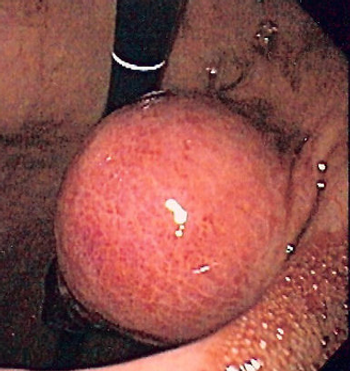
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors have until recently had a uniformly poor prognosis with lack of effective drug therapies. These tumors usually have activating mutations in either KIT or PDGFR-α tyrosine kinase receptors. Over the past decade, imatinib (Gleevec), a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor has become the standard of care for the first-line treatment of patients with unresectable and metastatic disease. For patients with imatinib-resistant disease or intolerant to the side effects of imatinib, sunitinib (Sutent), a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor was recently approved. For earlier-stage disease, status post–complete surgical excision, preliminary data seem encouraging for the role of adjuvant imatinib in prolonging patients' disease-free interval. The impact of neoadjuvant drug therapy needs to be further classified and explored. With additional evaluation of other tyrosine kinase inhibitors and novel therapies against other molecular markers, the treatment paradigm for this malignancy should continue to evolve.

Pain in older cancer patients is a common event, and many times it is undertreated. Barriers to cancer pain management in the elderly include concerns about the use of medications, the atypical manifestations of pain in the elderly, and side effects related to opioid and other analgesic drugs. The care of older cancer patients experiencing pain involves a comprehensive assessment, which includes evaluation for conditions that may exacerbate or be exacerbated by pain, affecting its expression, such as emotional and spiritual distress, disability, and comorbid conditions. It is important to use appropriate tools to evaluate pain and other symptoms that can be related to it. Pain in older cancer patients should be managed in an interdisciplinary environment using pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions whose main goals are decreasing suffering and improving quality of life. In this two-part article, the authors present a review of the management of pain in older cancer patients, emphasizing the roles of adequate assessment and a multidisciplinary team approach.

Despite the high prevalence of brain metastases in patients with metastatic lung cancer, these patients have been excluded from enrollment in clinical trials of new therapeutic drugs. The reasons for exclusion have centered on concerns that the blood-brain barrier may impede drug delivery into brain metastases, that brain metastases confer a dismal survival for metastatic lung cancer patients, and that brain metastases carry risk for cerebrovascular hemorrhage. A focused, updated review of these issues, however, clearly shows that these particular concerns are unwarranted. An extensive review of clinical trials on the efficacy of chemotheraputic agents against lung cancer brain metastases is also provided. This collective information describes an area in need of therapeutic development and supports an initiative to evaluate novel targeted therapies for lung cancer brain metastases.