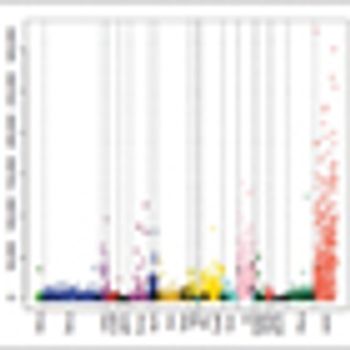
While continuing to warn against use of laparoscopic power morcellators for the removal of uterus or uterine fibroids in most women, the FDA is allowing the marketing of a containment system for use with certain power morcellators to isolate tissue not suspected to be cancerous.