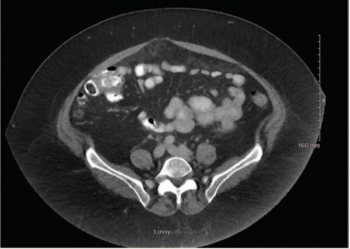
Mehmet Sitki Copur, MD, and colleagues examine the case of a 65-year-old patient with appendiceal mucinous neoplasms of the appendix who was treated with cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Mehmet Sitki Copur, MD, and colleagues examine the case of a 65-year-old patient with appendiceal mucinous neoplasms of the appendix who was treated with cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy.
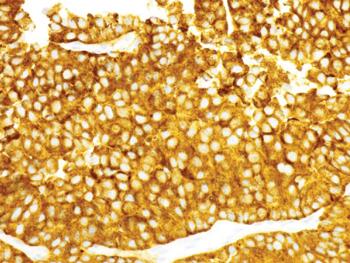
Abstract: Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms. They can be functioning tumors with secretion of a variety of peptide hormones, or nonfunctioning tumors with metastases to the liver at the time of diagnosis. Well-differentiated tumors tend to be slow-growing and characterized by low tumor mutational burden (TMB) and lower propensity to express PD-L1. Hypercalcemia due to malignancy can occur in about 20% to 30% of patients with cancer. The secretion of parathyroid hormone–related protein (PTH-rP) is among the causes of malignant hypercalcemia and has seldom been associated with hypercalcemia of NETs. Although the therapeutic landscape for neuroendocrine neoplasms has evolved substantially over the past decade, the role of immunotherapy has not yet been completely explored in this group of patients. We present a rare case of a metastatic pancreatic NET with high TMB, high PD-L1 tumor proportion score, and high PTH-rP–related hypercalcemia.
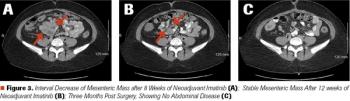
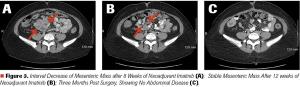
ABSTRACT Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are rare neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract. They commonly present with nonspecific symptoms and thus are often discovered incidentally. They are best identified by CT scan and most stain positive for CD117 (C-Kit), CD34, and/or DOG-1. Several risk stratification classification systems have been developed based on tumor size, mitotic rate, location, and perforation. Traditional chemotherapy and radiation therapy have been very ineffective, making surgery the mainstay of treatment. The discovery of mutations associated with these tumors has revolutionized the treatment approach. Imatinib mesylate, a selective tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitor, used as adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapy, has greatly improved the morbidity and mortality associated with GISTs. As the survival of patients has increased with the long-term use of targeted therapies, quality-of-life issues now have become much more relevant and have come to the forefront of care. We present a young woman who was successfully treated for GIST but now faces associated long-term adverse effects of imatinib, including the challenge of preserving fertility and the potential for childbearing.
Published: August 11th 2020 | Updated: