This study explores the efficacy and safety of combining docetaxel and capecitabine for treating recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


This study explores the efficacy and safety of combining docetaxel and capecitabine for treating recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer.
A review of the role of immune therapy in HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, along with the evidence and perspective behind differing therapeutic considerations.
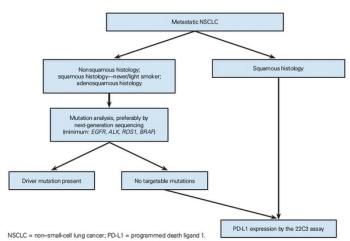
In this article, an approach to the diagnostic evaluation of patients with newly diagnosed advanced NSCLC is suggested, in an attempt to identify the best treatment options.

In this video, Apar Ganti, MD, highlights recent advances and studies presented at ASCO 2018 on management of NSCLC and SCLC with ICIs and targeted agents.

This article reviews the pathology and current evidence on systemic therapies for the management of advanced salivary gland cancers that are not amenable to local therapy.
Exciting advances in understanding the biology of lung cancer have occurred over the last few years.

Despite a decreasing incidence in the United States, small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) remains a major clinical problem, with approximately 30,000 new cases each year. The diagnosis of SCLC is usually not difficult. The Veterans Administration Lung Study Group (VALSG) staging system is less accurate than the American Joint Committee of Cancer tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) system (7th edition) at predicting survival in SCLC, especially in lower stage disease. Surgery has not played a major part in the management of SCLC, but emerging data suggest that resection may have a role in earlier stage disease. While the frontline treatment of SCLC has not changed significantly in the past decade, newer agents that are currently being investigated provide hope for better treatment of relapsed/refractory disease for the future.

Almost 40% of patients with newly diagnosed small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) have disease confined to the ipsilateral hemithorax and within a single radiation port, ie, limited-stage disease. The median survival for this group of patients after treatment is approximately 15 months, with one in every four patients surviving 2 years. Current optimal treatment consists of chemotherapy with platinum/etoposide, given concurrently with thoracic radiation. Surgery may represent an option for very early-stage disease, but its added value is uncertain. Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is used for patients with limited-stage SCLC who have achieved a complete response following initial therapy, as it decreases the risk of brain metastases and provides an overall survival benefit. Newer targeted agents are currently being evaluated in this disease and hold the promise of improving current outcomes seen in patients with early-stage disease.

The role of screening in order todetect lung cancer at an earlierstage has been widely debatedfor the past 4 decades. In this review,Dr. Mulshine focuses on the currentissues in lung cancer screening in lightof the findings of the InternationalEarly Lung Cancer Action Project(I-ELCAP) As the article mentions, thediagnosis of lung cancer is often madeat a stage when the disease is no longer amenable to cure. This is probably themost important cause for the dismaloutcomes of patients with lung canceroverall.

The most common indolent lymphoma, follicular lymphoma comprises 35% of adult non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) in the United States and 22% worldwide. Features associated with adverse outcome include age, male gender, disease stage, and performance status, with the International Prognostic Index being the most widely used risk classification system. Long-term disease-free survival is possible in select patient subgroups after treatment, but very late relapses suggest that quiescent lymphoma cells might be harbored for long periods of time. Radiation therapy is the mainstay of treatment for limited-stage follicular lymphoma, but there is some experience with chemotherapy and combined chemoradiation. When to initiate treatment in patients with advanced disease is controversial, but options include various combined chemotherapy regimens, monoclonal antibodies, radiolabeled antibodies, and bone marrow or stem cell transplantation. Future directions in the treatment of follicular lymphoma include vaccines, antisense therapy, and proteasome inhibitors.
Published: August 13th 2025 | Updated:

Published: October 15th 2010 | Updated:
Published: January 15th 2011 | Updated:

Published: March 1st 2007 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 2005 | Updated:

Published: February 1st 2005 | Updated: