
In this article, important concepts in the molecular testing of non–small-cell lung cancer are highlighted.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


In this article, important concepts in the molecular testing of non–small-cell lung cancer are highlighted.
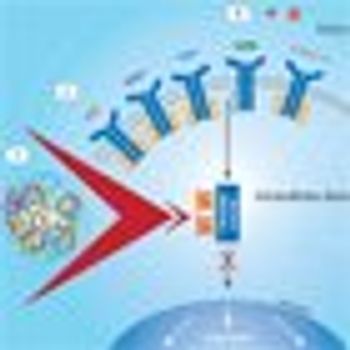
This review will describe the well-known use of VEGF antibodies; the current uses of EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors; newer agents being used against MET, FGFR, and other intracellular targets; insights regarding the field of immunotherapy in lung cancer; and finally, newer developments in chemotherapy.

In this issue of Oncology, Levy and colleagues provide a comprehensive review of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma [BAC], with a focus on the management of this rare disease, which represents 4% of all lung cancers.[1] The definition of BAC was revised by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2004, with changes made to the diagnostic criteria and classification.[2] BAC was defined as an adenocarcinoma of the lung that grows in a lepidic fashion along the alveolar septa without invasion of stroma, blood vessels, or pleura. BAC has been sub-classified into three types: nonmucinous, mucinous, and mixed.

Published: May 15th 2013 | Updated:

Published: September 15th 2010 | Updated:
Published: April 15th 2019 | Updated: