
This slide show highlights some of the top breast cancer news of 2016, including a study looking at optimal margins in DCIS, a trial on biosimilars, a new FDA approval, and more.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!



This slide show highlights some of the top breast cancer news of 2016, including a study looking at optimal margins in DCIS, a trial on biosimilars, a new FDA approval, and more.

Polymorphisms in the FCGR3A gene are correlated with degree of benefit from trastuzumab in women with ERBB2/HER2-positive breast cancer, according to a new analysis.

Serum levels of a vitamin D biomarker measured at the time of breast cancer diagnosis were independently associated with breast cancer prognosis, especially among premenopausal women.

The antibody-drug conjugate trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) showed non-inferior-but not superior-efficacy to trastuzumab plus a taxane in women with advanced HER2-positive breast cancer.

Tailored dose-dense chemotherapy in high-risk early breast cancer patients did not show a significant improvement in recurrence-free survival compared with standard adjuvant chemotherapy.

Stratifying breast cancer patients by chemotherapy and genetic susceptibility, researchers were able to identify patients at high risk of venous thromboembolism.

A new paper highlights the global inequities in access to prevention, early detection and treatment for breast cancer and cervical cancer.

A cognitive rehabilitation program known as Insight resulted in improvements in cognitive symptoms compared to standard care in adult cancer survivors.

Two new studies are suggesting that PIM1 inhibitors, which are already in clinical trials for leukemia and multiple myeloma (MM), may help combat triple-negative breast cancer.

The initiation of and adherence to tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors (AIs) such as anastrozole is low among older women with estrogen receptor-positive ductal carcinoma in situ.

The presence of circulating tumor cells at baseline was associated with decreased overall and disease-free survival in patients with inflammatory breast cancer undergoing treatment with neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with bevacizumab.

Use of tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors therapy during and after breast cancer treatment were found to reduce the risk of contralateral breast cancer in a community healthcare setting.

Peregrine Pharmaceuticals has announced preliminary findings from preclinical research showing that antiphosphatidylserine (PS) antibodies “similar to bavituximab” improves anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade’s antitumor activity in a mouse model of triple-negative breast cancer.

In patients with HER2-positive breast cancer undergoing trastuzumab therapy, elevated troponin I or T before the treatment is associated with an increased risk of trastuzumab-related cardiac dysfunction.

Fulvestrant (Faslodex) has demonstrated significant increases in progression-free survival in women with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer.

Common breast cancer risk alleles are correlated with both the incidence of breast cancer and mortality, and using these alleles along with other factors could identify women at very low risk of breast cancer who could potentially avoid mammography.

Response to the HER2-targeted therapies lapatinib and trastuzumab are correlated with pathway-level genetic alterations, but not specific gene mutations.

Venous thromboembolism is significantly more likely over the long term in breast cancer patients than in the general population, according to a study in Sweden.

Here we review current guidelines on breast and ovarian cancer screening, prophylactic surgery, and other risk-reduction strategies in patients with these mutations, and we detail the data that drive these recommendations.
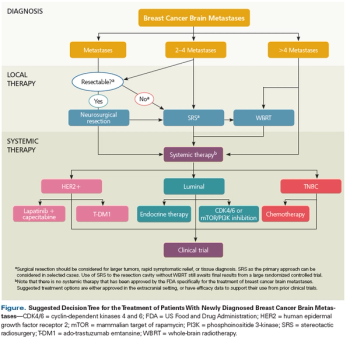
This review summarizes the most up-to-date approach to the multidisciplinary management of patients with breast cancer brain metastases.

For some time, genetic testing has been predictive and prognostic. It is now assuming a therapeutic role as well. An example is the targeting of breast cancer patients with BRCA mutations for treatment with PARP inhibitors.

Brain metastasis remains a relatively common and particularly devastating complication of breast cancer and has proven a particularly challenging area for therapeutic innovation.

Adding ribociclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, to letrozole significantly improved progression-free survival in postmenopausal women with advanced, HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer.

Breast cancer tumors that are HER2-negative can spontaneously flip, with populations of circulating HER2-positive cells, suggesting treatment strategy.

Circulating breast tumor cells from patients can convert from HER2-negative to HER2-positive according to a study published in Nature.