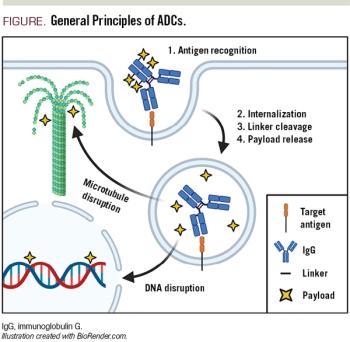
ABSTRACT: Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) comprise a unique class of chemoimmunotherapy agents, incorporating cytotoxic payloads covalently linked to a monoclonal antibody via specialized linkers. This strategy attempts to exploit antibody-antigen specificity to selectively deliver a potent ‘warhead’ payload to tumor cells (Figure), while sparing nontumor antigen-negative cells. Decades of development have culminated in the recent approvals of a handful of ADCs across multiple tumor types. ADCs for the treatment of lymphoma are particularly attractive due in part to the favorable spectrum of cell surface markers uniquely expressed on lymphocytes compared with other tissues. Here we discuss general principles of ADC design, including antigen/antibody, payload, and linker selection. We highlight the clinical successes of the 2 approved ADCs for treatment of lymphomas: brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) and polatuzumab vedotin (Polivy). Finally, we describe several ADC agents currently under development for lymphoma, including emerging efficacy and toxicity data from early-stage clinical trials.