Persistent Erythematous Papular Lobulated Masses on Patient’s Nose
A 90-year-old man presented with a 6-month history of swelling and redness of his nose. He had persistent erythematous macules, plaques, and partially confluent nodules with irregular borders developing on his nose over the past 6-month period. What is your diagnosis?
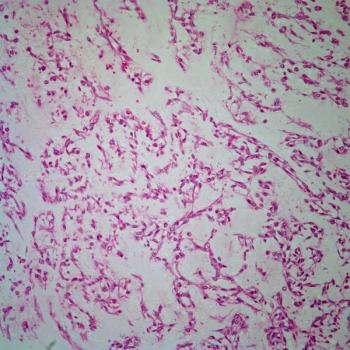
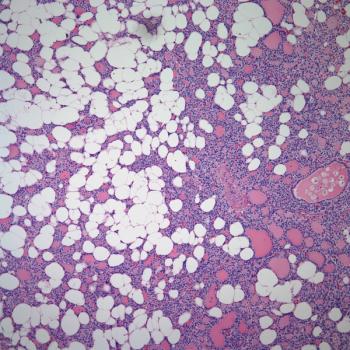
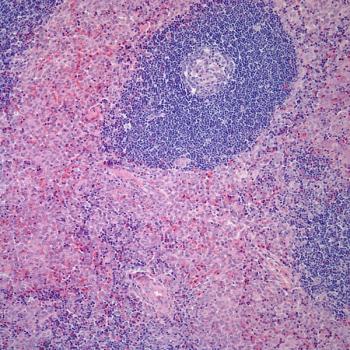
A 90-year-old man presented with a 6-month history of swelling and redness of his nose. He had persistent erythematous macules, plaques, and partially confluent nodules with irregular borders developing on his nose over the past 6-month period. He was initially seen by his dermatologist and treated with antibiotics and steroids, but with no major improvement. Physical examination revealed large, infiltrative, edematous, erythematous plaques and rare nodules, with superficial telangiectasia, but was negative for pathologic lymphadenopathy or organomegaly. Routine laboratory analysis was normal. A punch biopsy of the nose lesion was performed, revealing atypical proliferative cells infiltrating the skin in many areas, with a poorly vasoformative pattern. Immunohistochemical stain was positive for CD31.
What is your diagnosis?
Newsletter
Stay up to date on recent advances in the multidisciplinary approach to cancer.