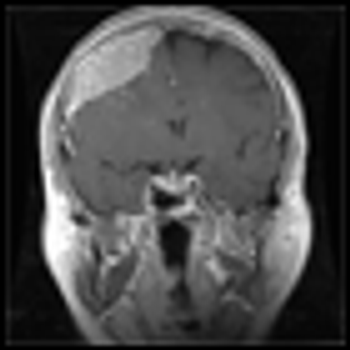
Intracranial neoplasms can arise from any of the structures or cell types present in the cranial vault, including the brain, meninges, pituitary gland, skull, and even residual embryonic tissue.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Intracranial neoplasms can arise from any of the structures or cell types present in the cranial vault, including the brain, meninges, pituitary gland, skull, and even residual embryonic tissue.

Intracranial neoplasms can arise from any of the structures or cell types present in the cranial vault, including the brain, meninges, pituitary gland, skull, and even residual embryonic tissue. The overall annual incidence of primary brain tumors in the United States is 14 cases per 100,000 population.

Brain metastases are the most common type of brain tumor in adults and are an increasingly important cause of morbidity and mortality in cancer patients. In recent years, important advances have been made in the diagnosis

Each year more than 100,000 cancer patients in the United States develop brain metastases [1]. Of these, the majority will have either multiple lesions or uncontrolled primary or metastatic disease [2-4]. The treatment and care of patients with brain metastases remains a serious health-care problem. The article by Berk is a comprehensive review of completed or ongoing clinical trials worldwide evaluating the role of radiotherapy in the treatment of patients with brain metastases.

Published: March 11th 2010 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 1995 | Updated:
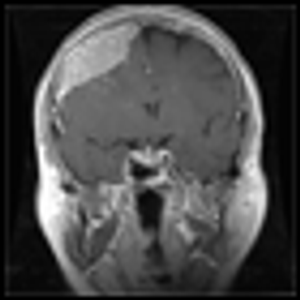
Published: November 1st 2015 | Updated:

Published: July 1st 1999 | Updated: