
The emergence of immune checkpoint inhibitors as effective cancer immunotherapy has effectively built a new “highway” connecting the promise of oncologic translational research to progress in treating advanced malignancies.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The emergence of immune checkpoint inhibitors as effective cancer immunotherapy has effectively built a new “highway” connecting the promise of oncologic translational research to progress in treating advanced malignancies.

In this interview we discuss predictive biomarkers and response to immune checkpoint inhibitors for urothelial tumors, which include tumors of the bladder, ureters, and the renal pelvis.

An observational study found that adjuvant chemotherapy improves overall survival in patients with locally advanced bladder cancer.

Despite a high rate of hematologic toxicity, combined low-dose gemcitabine (Gemzar), paclitaxel, and sorafenib (Nexavar) showed promise as a well-tolerated salvage therapy in a small group of patients with cisplatin-resistant urothelial cancer.

An Egyptian study found that bladder cancer patients who underwent radical cystectomy had better local recurrence-free survival with adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy combined, compared with chemotherapy alone.

The anti-PD-L1 antibody atezolizumab showed significantly improved objective response rates compared to historic controls in a phase II study of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma previously treated with platinum-based therapy.

Comprehensive genomic profiling of patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma has revealed a very high frequency of clinically relevant genomic alterations.

Patients with metastatic or unresectable urothelial carcinoma who are treated with either carboplatin or cisplatin have high rates of vascular thromboembolic events.

A phase II trial found that use of a personalized peptide vaccination improved overall survival in patients with chemotherapy-resistant advanced urothelial bladder cancer.

In most cases, localized small-cell bladder cancer requires cystectomy for optimal cure rates.

Radiation therapy with concurrent chemotherapy is an effective treatment strategy for small-cell bladder cancer.

Use of the diabetes drug pioglitazone was not associated with a significantly increased risk of bladder cancer, in a large cohort study.
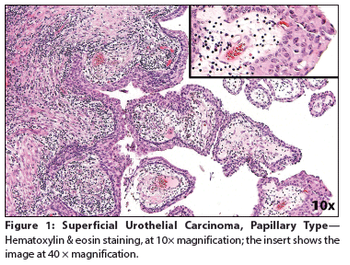
A 65-year-old woman presented to a local emergency department complaining of right flank pain that had worsened over the past 10 days. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis showed intravesical tumors of the urinary bladder.

Pembrolizumab demonstrates durable antitumor activity in patients with advanced urothelial cancer, with a higher response rate seen in patients with PD-L1 expression.

Advanced bladder cancer patients with poor prognosis appear to benefit from adding apatorsen 600 mg to first-line chemotherapy with gemcitabine/cisplatin.

Presentation with a urinary tract infection delayed a bladder cancer diagnosis among a population of Medicare patients, with worse delays experienced by women.
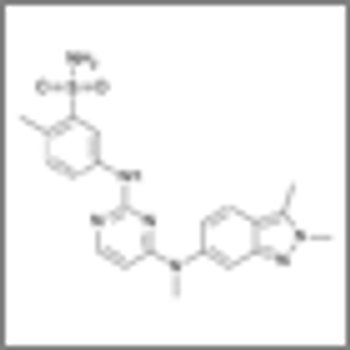
Phase II study results found that half of patients with relapsed or refractory urothelial carcinoma responded to treatment with pazopanib and paclitaxel.

In this interview we discuss the changing landscape of systemic therapies for the treatment of bladder cancer.
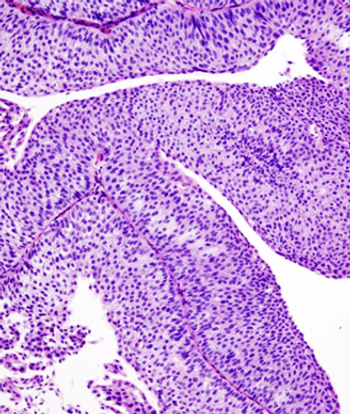
Patients with bladder cancer derived an overall survival benefit from the use of adjuvant chemotherapy compared with observation.

A urine test (CellDetect) was able to detect disease recurrence in bladder cancer patients, with a reported sensitivity of 84.4% and specificity of 82.7%.

While observation may be appropriate for select cases where prognosis is poor, rates of non-treatment are unacceptably high in muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Long-term survival rates of patients after laparoscopic surgery for bladder cancer are similar to rates achieved with standard open surgery.

An extremely large database study across more than one million people found no increased risk of bladder cancer with the diabetes drug pioglitazone.

A large phase I study showed that the PD-L1 antibody known as MPDL3280A has promising activity in patients with urothelial bladder cancer.

Cancer survivors are at an increased risk for developing a second smoking-associated cancer if they smoked cigarettes prior to their first cancer diagnosis.