
University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute researchers have discovered a previously unknown virus strongly associated with Merkel cell carcinoma, a rare but aggressive skin cancer that typically affects elderly and immunosuppressed individuals

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute researchers have discovered a previously unknown virus strongly associated with Merkel cell carcinoma, a rare but aggressive skin cancer that typically affects elderly and immunosuppressed individuals

In a surprising discovery, reported at RSNA 2007, researchers from Germany have found that whole-body staging of patients with recently diagnosed malignant melanoma using either MRI or PET/CT could miss a substantial number of metastatic lesions

Schering-Plough Corporation has announced that FDA has granted priority review to its supplemental Biologics License Application for Pegintron (pegylated interferon alfa-2b) as adjuvant therapy for patients with stage III melanoma.

US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted the peginterferon alfa-2b (PEG-Intron) supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) for for review and has granted Priority Review status to the drug for the adjuvant treatment of patients with stage III melanoma

A new type of agent, an oxidative stress inducer, combined with paclitaxel improved survival in patients with metastatic melanoma, compared with paclitaxel alone

GSK and Synta announce STA-4783 collaboration

Integrins have direct effects in stimulating proliferation and preventing apoptosis in cancer cells and mediating proangiogenic interactions between endothelial cells and extracellular matrix. Alterations of expression of various integrins and their receptors have been observed in various cancers in which angiogenesis is known to play a role, including colorectal cancer. Inhibition of specific integrins might thus inhibit both direct effects of integrins on cancer cells and tumor angiogenesis. Inhibitory peptides and anti-integrin monoclonal antibodies are currently being investigated in clinical trials in patients with solid tumors, with early evidence suggesting clinical benefit in disease stabilization with use of an anti-αvβ3 antibody in the settings of colorectal cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Integrin inhibition alone and with other targeted therapeutic approaches should be further investigated in clinical trials in patients with colorectal cancer.

Integrins play an important physiologic role in cell adhesion, and accumulating evidence suggests that they also regulate cell growth, proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. A number of congenital and acquired disease states have been associated with integrins, and small- molecule integrin inhibitors have been approved for treatment of benign hematologic diseases. In cancer, aberrant expression with normal functioning rather than dominant genetic variations of genes coding for integrins has generally been observed. This aberrant expression is mediated through "bidirectional" receptor signaling and interaction with corresponding signals from growth factor signaling pathways, leading to inhibition of apoptosis, induction of cell proliferation, extracellular matrix remodeling, migration, and angiogenesis. From a clinical perspective, a growing number of molecules targeting integrins have been developed for treatment and imaging purposes; clinical studies in melanoma, prostate cancer, and other malignancies are underway. This review summarizes the biology of integrins, the signal transduction pathways they regulate, and their role in different stages of carcinogenesis. Furthermore, it provides a synopsis on the clinical advancements in integrin targeting for therapeutic and imaging purposes in cancer.

When you inspect moles, pay special attention to their sizes, shapes, edges, and color. A handy way to remember these features is to think of the A, B, C, and D of skin cancer-asymmetry, border, color, and diameter.

Since its inception in 1985, the American Academy of Dermatology's National Melanoma/Skin Cancer Screening Program has screened more than 1.7 million people and detected more than 171,200 suspicious lesions. More than 20,000 of these lesions were suspected melanomas—the most serious form of skin cancer.

Genta Incorporated has announced that the company will conduct a new randomized controlled phase III trial of its lead anticancer product Genasense (oblimersen sodium) Injection in patients with advanced melanoma.

Hepatic Arterial Chemoembolization (HACE) May Prolong Survival in Melanoma Patients With Liver Mets

May is National Skin Cancer Awareness MonthWhat Is Your Skin Cancer IQ?Identifying BCC, SCC, and melanoma

At follow-up of more than 2 years, the largest study ever conducted in patients with advanced melanoma has continued to show a trend toward improved survival and a near-doubling of both progression-free survival (PFS) and durable response rates when the targeted antisense drug oblimersen sodium (G3139, Genasense) was added to standard therapy with the alkylating agent dacarbazine (DTIC).

Bayer Pharmaceuticals Corporation and Onyx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Emeryville, California) have announced that a phase III trial administering sorafenib (Nexavar) or placebo tablets in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with advanced melanoma did not meet its primary endpoint of improving progression-free survival. The treatment effect was comparable in each arm.

Five of seven advanced melanoma patients had significant regression or stabilization of disease after treatment with Ontak (denileukin diftitox, Eisai)

Two of 15 patients with metastatic melanoma had tumor regression after treatment with genetically modified peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs)

A Mayo Clinic physician and his colleagues have defined the normal number of melanocytes that are present in Caucasians' sun-exposed skin.

Talabostat (PT-100, Point Therapeutics), an oral, small-molecule inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP) fast-tracked by the FDA for stage IIIB/IV non-small-cell lung cancer, also looks promising in salvage regimens for patients with advanced melanoma or chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL
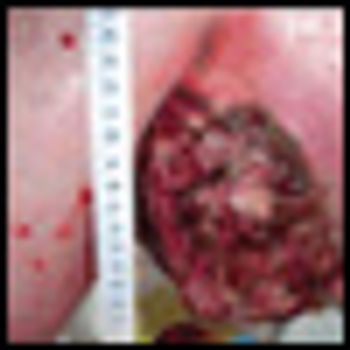
The patient is an otherwise healthy male transferred from an outside hospital with a newly diagnosed melanoma from an unknown primary presenting as a large, left axillary mass.

During the past 18 months, researchers have developed substantial evidence supporting the notion that stem cells play a critical role in the development of at least some cancers, their progression, and the prognosis of patients, including breast, brain, lung, and prostate cancer, multiple myeloma, and melanoma.

On May 6, members of the American Academy of Dermatology (ADA) hope to set a Guinness World Record for the most people screened for skin cancer in a single day.

According to a 2005 survey conducted by the American Academy of Dermatology, 92% of the respondents understood that getting a tan from the sun is dangerous. Yet, 65% said that they think they look better when they have a tan.

ORLANDO-Adding the investigational antisense agent oblimersen sodium (Genasense, G3139) to dacarbazine (DTIC) significantly improved response and survival in patients with advanced malignant melanoma in a phase III trial. John M. Kirkwood, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute, reported 2-year results at the 41st Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (abstract 7506) (see Table).

Mohs surgery has been well-established as the gold standard for the treatment of BCCs and SCCs. And, as described in this article, preliminary reports suggest that it may play an equally important role in the management of several other cutaneous malignancies.