
T-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas are a heterogeneous group of diseases that differ markedly in terms of their clinical behavior and prognosis. In recently developed classification systems, the sites of initial disease

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


T-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas are a heterogeneous group of diseases that differ markedly in terms of their clinical behavior and prognosis. In recently developed classification systems, the sites of initial disease

recent teleconference sponsored by Cancer Care Inc centered on newer treatments for aggressive lymphomas. Michael Grossbard, MD,

Mycosis fungoides is an indolent primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) that usually progresses from localized skin lesions to systemic disease. Sézary syndrome is a distinct variant characterized by generalized

The increasing use of systemic and directed liver therapy for patients with hepatic metastases has created a demand for improved accuracy of noninvasive imaging techniques. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic

The management of hepatic tumors presents a challenging problem. The natural history of primary and metastatic liver lesions portends a poor prognosis. However, surgical resection and newer ablative techniques have had a

Either alone or in combination with other antineoplastics, fluorouracil (5-FU) has been the mainstay of treatment of gastrointestinal, breast, and head and neck cancers for the past 40 years. Numerous active 5-FU schedules are in

The criteria for successfully resecting pulmonary metastasis have not changed since they were originally described by Ehrenhaft in 1958.[1] They are (1) that the primary tumor site has been removed without evidence of local recurrence, (2) that no extrathoracic organ metastasis exists, and (3) that pulmonary disease has been completely removed without compromising pulmonary function.

In their literature survey, Drs. Chao and Goldberg reach the conclusion that surgical metastasectomy is the clear treatment of choice and should be the standard of care for patients with pulmonary recurrences of soft-tissue sarcoma. It is assumed that survival without this operation is negligible, even while there are no survival statistics for sarcoma patients who are eligible for metastasectomy and who choose to forgo this option.

The lung is the most frequent site of metastasis from soft-tissue sarcomas. Due to the relative resistance of sarcoma to either chemotherapy or radiotherapy, compared to other solid tumors, surgical management of

In their article, Chao and Goldberg provide a concise overview of the literature on pulmonary metastasectomy for sarcoma, including a brief history of the procedure, guidelines for preoperative evaluation, conduct of the operation, and probable outcomes achieved. Several points that they review deserve further discussion.

The borderline category of ovarian tumors is one of the most controversial topics in gynecologic oncology and pathology, and is confusing to both clinicians and patients. Although numerous reviews have appeared in the literature, most of them rehash the prevailing views on borderline tumors without critically evaluating the published data that allegedly validate some rather puzzling and perplexing notions. For example, although these tumors are considered to be a subset of carcinoma, most patients are cured even when they have “metastatic” disease that has been inadequately treated. In addition, reports cite recurrence and death as late as 39 years after the diagnosis of tumors that appear histologically bland and noninvasive.

Ovarian tumors of low malignant potential (LMP) would benefit from a new name, not to mention a deeper understanding of their biology, effective treatment, and a framework within which they can be studied. Fortunately, for a pathologic entity that is poorly understood and also is unresponsive to current therapy, most LMP ovarian tumors carry a benign prognosis.

Low malignant potential (LMP) ovarian tumors represent a small subset of epithelial ovarian cancers that were first identified 70 years ago but were recognized in a systematic way only within the last 30 years. These lesions

The article by Damjanov and Meropol elegantly outlines the rationale behind the preclinical development of several potential new oral chemotherapy options for patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma and the available data from clinical trials in advanced colorectal cancer that evaluated the activity and safety of these agents. The authors relate the history of fluorinated pyrimidine therapy in colorectal cancer and the pharmacologic challenges to delivering effective oral therapy in a such a way that the chemistry behind the processes becomes readily intelligible. They note that the erratic absorption and blood levels associated with orally administered fluorouracil (5-FU) led to the current approaches to oral therapy.

The US Food and Drug Administration has approved ALZA Corporation’s new drug application for a

Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the world’s most common cancers. It is closely associated with cirrhosis, especially that due to viral hepatitis. The incidences of viral hepatitis and HCC are rising steadily in the United

Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) is the most common malignancy associated with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Recent years have witnessed a decline in the overall incidence of AIDS-related KS, as well as a greater

Pentostatin (Nipent) has demonstrated significant activity as a single agent in patients with low-grade B- and T-cell lymphomas, but thus far, clinical experience with combinations of pentostatin and other agents is limited. A study
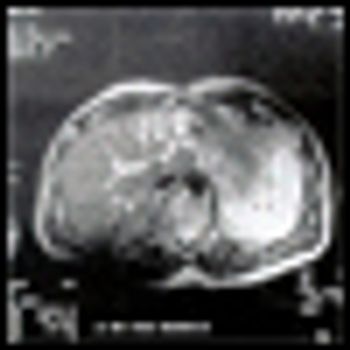
In this short review, we describe two new liver-specific contrast agents for MRI that are in clinical development. The main differences among the liver-specific contrast agents available at present are also discussed briefly.