
A new study yielded nomograms for the assessment of locally advanced cervical cancer, with prognostic factors including histology, performance status, and others.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A new study yielded nomograms for the assessment of locally advanced cervical cancer, with prognostic factors including histology, performance status, and others.

Cervical cancer survivors saw improvements in self-reported quality-of-life outcomes with a psychosocial telephone counseling intervention, according to a new study.
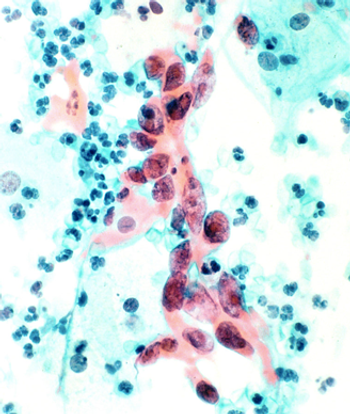
Women in routine gynecologic care expressed willingness to extend screening intervals and use cytology alone or Pap-HPV cotesting if recommended by a physician.
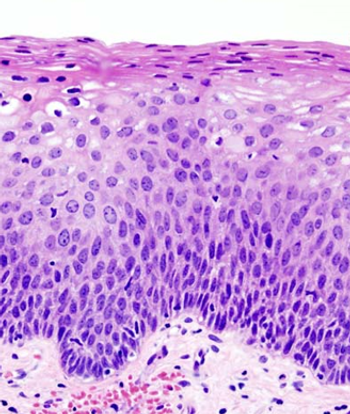
Conservative management of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) grade 2 is an appropriate treatment option for women aged 25 years and younger.
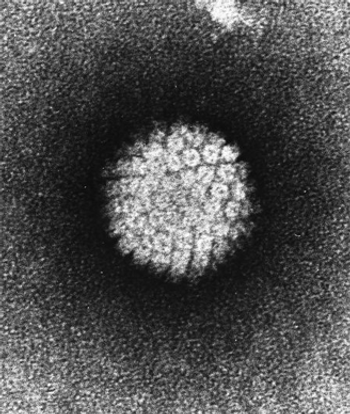
A test for dangerous strains of high-risk HPV using messenger RNA was shown to be reliable and effective for cervical cancer risk stratification.
Multiple lesion-directed biopsies can drastically improve the sensitivity of colposcopy in women referred for abnormal cervical cancer screening.
More than 11% of all eligible women had not been screened for cervical cancer in the past 5 years, according to a study by researchers at the CDC.

Nurses trained in the visual inspection with acetic acid cervical cancer screening method were able to successfully perform colposcopy and detect cervical lesions.
Vaccines including that for HPV, which helps prevent cervical cancer, show no association at all with multiple sclerosis or other CNS demyelinating syndromes.
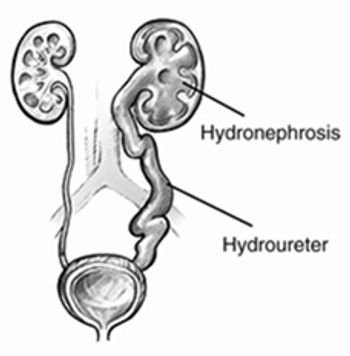
Hydronephrosis is associated with substantial morbidity in patients with cervical cancer, and is potentially associated with poorer survival as well.
A new human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine that protects against nine types of HPV and would protect against about 90% of cervical cancers could be available in 2015.
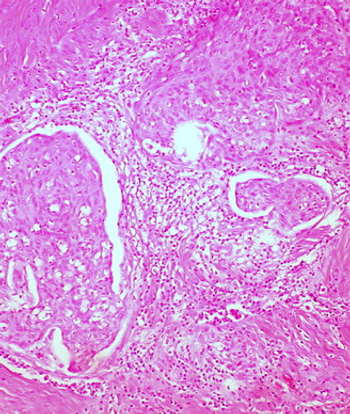
Adding the TKI cediranib to chemotherapy improved progression-free survival in patients with metastatic or relapsed cervical cancer, according to a study presented at the 2014 ESMO Congress.

The US Food and Drug Administration has approved bevacizumab (Avastin) for the treatment of patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer.

In light of the recent FDA approval of HPV testing for women as a screening method for cervical cancer, we discuss changing guidelines with two experts.

The FDA has approved an HPV DNA test to be used as a primary screening method for cervical cancer in women 25 and older. The test can also give insight into future risk of cervical cancer.

An FDA panel has recommended that a DNA test that screens for HPV in women can replace the standard Pap smear as a first-line primary cervical cancer screening test.
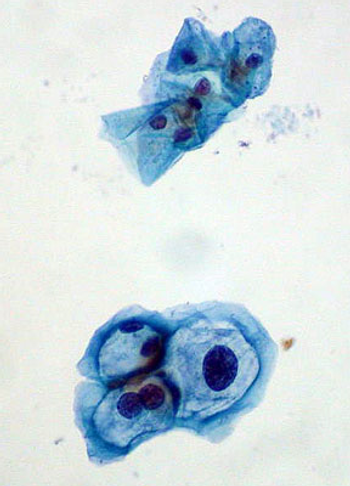
A new study has demonstrated that a therapeutic vaccine against HPV can stimulate an immune response and regression of high-grade cervical dysplasia, a precursor to cervical cancer in women with an HPV infection.

An analysis of four randomized clinical trials from Europe shows that HPV-based screening resulted in a greater long-term protection from invasive cervical cancer compared with a Pap test.
Results from the phase III GOG 240 trial, presented at ASCO, showed the addition of bevacizumab (Avastin) to standard chemotherapy improved overall survival by nearly 4 months in women with advanced or relapsed cervical cancer.
Biennial visual inspection with acetic acid (vinegar) screening by trained public health workers significantly reduced cervical cancer mortality in a large cluster-randomized controlled trial conducted among thousands of women from poor neighborhoods in Mumbai, India.

In this interview we discuss HPV-associated cancers, which are on the rise, and the low vaccination coverage for HPV with Edgar Simard, PhD, MPH, senior epidemiologist of surveillance research, who studies the impact of prevention and screening on cancer incidence at the American Cancer Society.

There has been a decline in overall cancer screening among the US population. Only colorectal cancer screening rates met current screening goals. Cancer survivors specifically met current national screening goals with the exception of cervical cancer screening.
A new study finds that baseline testing for HPV can better predict long-term negative cervical cancer outcomes compared to a Pap smear.

The European Society of Gynaecological Oncology (ESGO) biennial meeting is taking place in Milan, Italy, and will run from September 11-14, 2011.
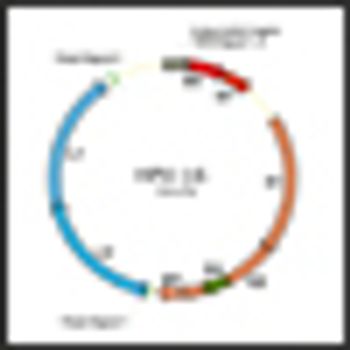
A study published in Lancet Oncology shows that an AS04-adjuvanted HPV 16 and HPV 18 vaccine developed by GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals can offer protection against anal cancer.