
In the VICTOR trial, patients with PI3KCA-positive colorectal cancer who took aspirin had a lower cancer recurrence compared to those with a wild-type PI3KCA gene.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


In the VICTOR trial, patients with PI3KCA-positive colorectal cancer who took aspirin had a lower cancer recurrence compared to those with a wild-type PI3KCA gene.

A study on screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancers, originally presented at ASCO 2013, found that from 1976 to 2009 late-stage cancer incidence decreased from 117 to 74 cases per 100,000 people, and early-stage incidence decreased from 77 to 68 cases per 100,000.

The use of a centralized nurse-led telephone-based care coordination system failed to improve outcomes including quality of life, unmet supportive needs or visits to the emergency department after surgical resection of colorectal cancer, according to the results of a new study.

Two separate studies have found direct evidence that F. nucleatum, a bacteria found in the mouth and in periodontal plaques, promotes growth of colorectal tumors.

Over the past few years, significant efforts have focused on developing and validating molecular biomarkers to better define the subset of patients with stage II disease who might derive benefit from adjuvant therapy.

At this juncture, various commercially available assays for colon cancer may be of little added value, and accelerated biomarker development with clinical validation is desperately needed.

In this review, we will discuss adjuvant chemotherapy in non-metastatic colon cancer, the existing prognostic and predictive molecular biomarkers in the field, and how to integrate these molecular biomarkers into the decision about whether to administer adjuvant therapy.

A new endoscopy technology called photometric stereo endoscopy, which captures the topography of the colon surface to create a 3D image, could be a more robust way to screen for precancerous lesions of the colon.

In this interview we discuss the role of aspirin in colorectal cancer prevention and treatment. Various studies have suggested that a daily aspirin pill can help prevent certain types of cancers. Other studies suggest that there may even be a role for aspirin in treating cancer.

A study of colorectal cancer survivors shows those who consume higher amounts of red and processed meats before a colorectal cancer diagnosis are at higher risk of death from any cause compared to those who eat less of both types of meat.

An analysis of two colorectal cancer studies found that patients with BRAF mutations were less sensitive to the effects of aspirin as treatment or prevention.
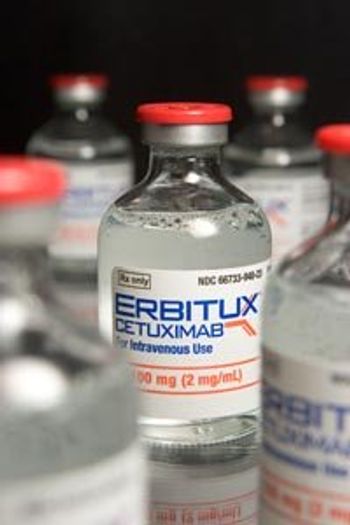
Results from the German AIO KRK-0306 study, FIRE-3, show that the addition of cetuximab (Erbitux) to chemotherapy rather than bevacizumab (Avastin) increased overall survival by nearly 4 months in patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer.

In this interview we discuss the advances in treatment for colorectal cancer, as well as ongoing developments to find new and better therapies to treat this type of cancer.

A large study shows that middle-age men engaged in lots of cardiovascular exercise have a reduced risk of developing and dying from lung and colorectal cancer.
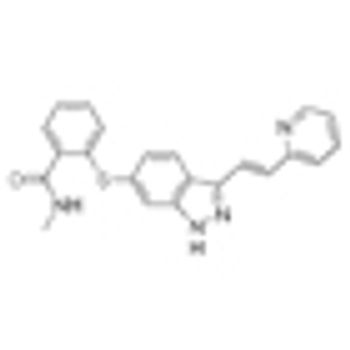
Adding the VEGF inhibitor axitinib to first-line treatment of FOLFOX-6 for metastatic colorectal cancer failed to improve progression-free and overall survival.
Women diagnosed with endometrial cancer at age 50 or younger had a fourfold increased risk for a subsequent colorectal cancer diagnosis, according to a historical cohort study published recently in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.

Patients with stage III colon cancer who have a history of smoking are more likely to have worse outcomes, according to a large, randomized phase III trial result.

Colorectal cancer patients testing positive for Lynch Syndrome on MSI and IHC were most likely to seek genetic counseling when contacted by a genetic counselor.

In a new study, researchers found that higher body mass index was associated with a risk of CTNNB1-negative colorectal cancer, while higher physical activity was associated with a lower risk for this type of disease.

An international group of researchers have collaborated on an unbiased genome-wide analysis of colorectal cancer, coming up with three distinct molecular subtypes that are potentially clinically relevant and are varying in their biology and clinical outcomes.
The same week that bevacizumab (Avastin) received a new indication for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer, results from two phase III trials involving the drug were presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2013 Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium (ASCO GI) held January 24–26 in San Francisco.

In this interview we discuss the latest treatments and research for gastrointestinal cancers with Dr. Cathy Eng, associate professor, department of gastrointestinal medical oncology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.

There has been a decline in overall cancer screening among the US population. Only colorectal cancer screening rates met current screening goals. Cancer survivors specifically met current national screening goals with the exception of cervical cancer screening.

Using a large genome-wide study of more than 28,000 individuals, three new genetic links to colorectal cancer have been identified, holding the potential for new therapeutic targets.

Initiating discussions about end-of-life care with patients with incurable cancers early in their disease was associated with a decrease in late-stage aggressive cancer treatments such as chemotherapy or acute care, and with an increase in the use of hospice care at the end of life.