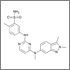
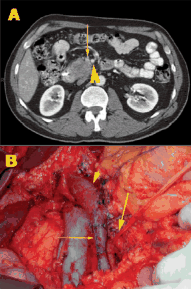
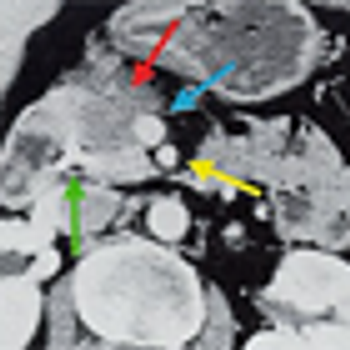
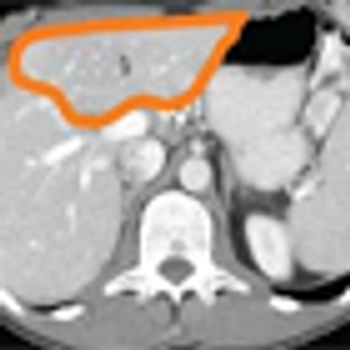
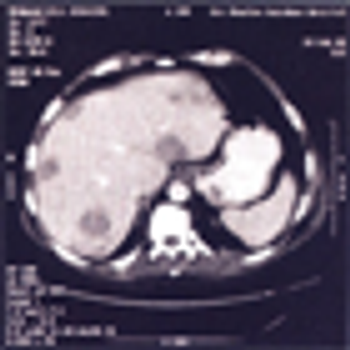
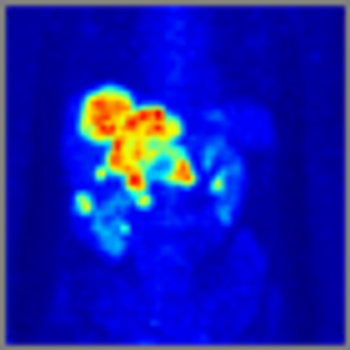
After 2 decades of disappointing phase III trials and years of single-agent gemcitabine therapy, the pancreatic cancer community is relieved to expand the front-line armamentarium in patients with mPAC. Here we evaluate the current landscape and ask some provocative questions about response rate, dosing, and predictive markers.