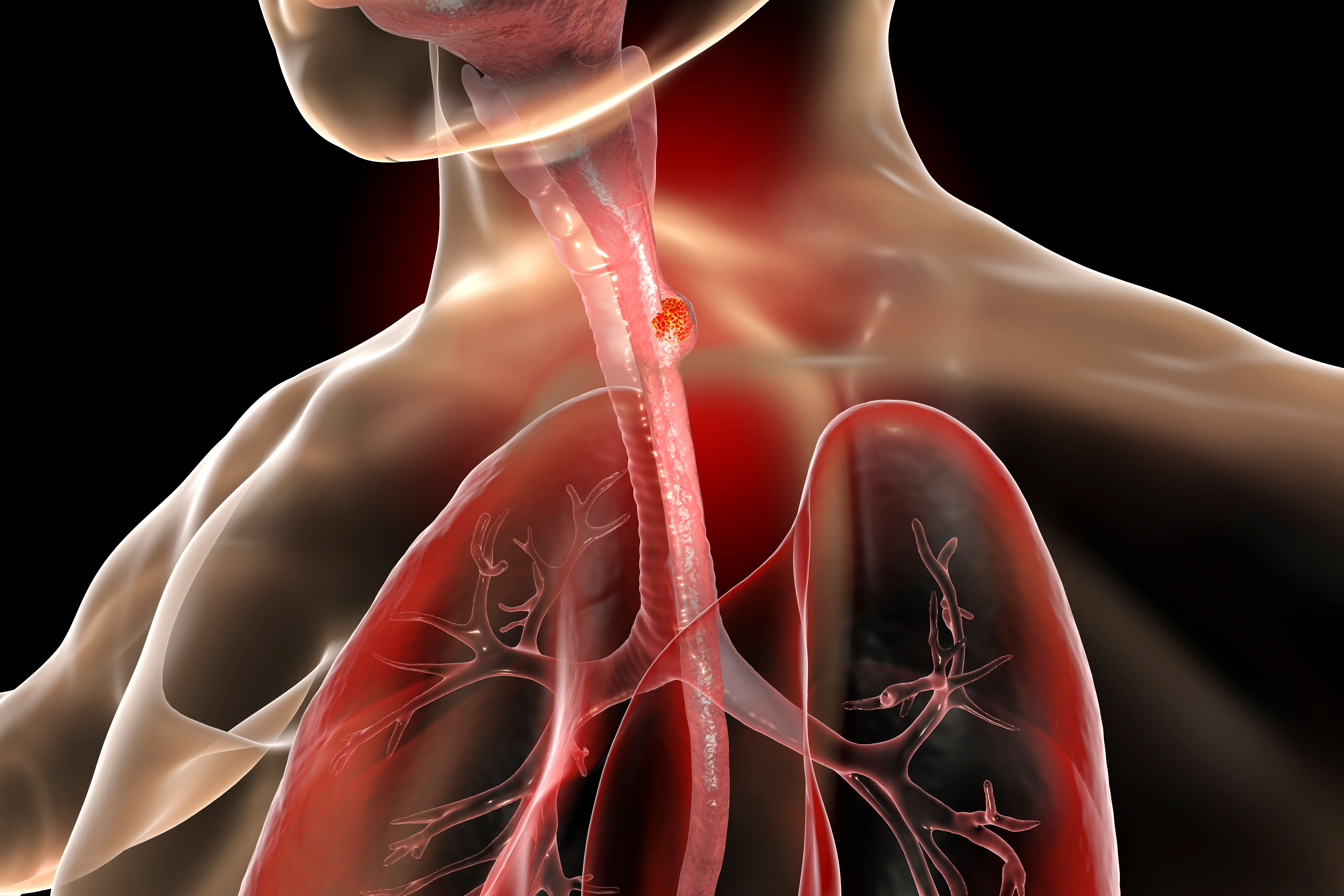
Esophageal Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos

Podcasts
CME Content
More News
Although radiotherapy was safe and well tolerated in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, more research is needed to confirm these results.

Patients with nonmetastatic esophageal cancer who received FLOT chemotherapy achieved a 3-year OS rate of 61.1% in an analysis of the phase 3 ESOPEC trial.
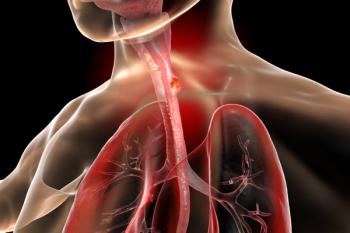
Subgroup data from RATIONALE-306 support the frontline use of tislelizumab plus chemotherapy in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Five-year follow-up confirms adjuvant nivolumab's sustained disease-free and distant metastasis-free survival benefits in resected esophageal/GEJ cancer post-CRT.
No fatalities were observed with fruquintinib plus camrelizumab, paclitaxel liposome, and nedaplatin when treating esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
The trial initiation is based on phase 1/2 IDeate-PanTumor01 trial results presented at the 2022 and 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
According to comparative single-cell transcriptome analyses, NOTCH1 deficiency facilitated a more immunologically active microenvironment in ESCC tumors.
Immunotherapy combinations and targeted therapy options may help bridge clinical gaps in early-stage, locally advanced, and metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinomas.
Postoperative complications and mortality after standard or postponed surgery for esophageal cancer after active surveillance were similar in both groups.

In the phase 2 EPOCI1802 trial, atezolizumab monotherapy elicited a cCR rate of 42.1%, an ORR of 65.8%, and a 12-month OS rate of 65.8% in advanced ESCC.

Data from the RATIONALE-306 trial support the approval of tislelizumab plus chemotherapy in unresectable or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.

Patients with esophageal cancer who received palliative care consultations during end-of-life treatment experienced a decreased financial burden compared with patients who did not.

Eleven votes were cast against the favorability of using anti–PD-1 inhibitors in patients with ESCC and a PD-L1 expression of less than 1.

The combination of perioperative chemotherapy plus FLOT improved overall survival vs neoadjuvant chemoradiation in patients with resectable esophageal cancer.

Results from the phase 3 RATIONALE 302 trial led to the approval of tislelizumab for patients with unresectable or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.

Investigators note that early interventions such as nutritional support and prehabilitation require further investigation to increase both the quality of life and overall survival for patients with esophageal cancer.
Data from the phase 3 SKYSCRAPER-08 trial may support tiragolumab plus atezolizumab and chemotherapy as an alternative frontline treatment option for those with locally advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Neoadjuvant camrelizumab plus chemotherapy may hold promise as a standard of care in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, according to Yin Li, MD.
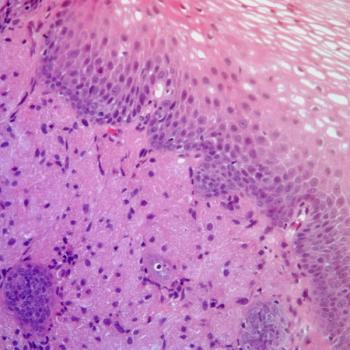
Sugemalimab is now approved for managing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in China following results from the phase 3 GEMSTONE-304 study.
Investigators will continue to assess the efficacy and safety of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab and chemotherapy as frontline treatment for patients with metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in part 2 of the LEAP-014 study.

Data from the NeoRes II trial caution against routinely delaying surgery for more than 6 weeks after patients with resectable locally advanced esophageal cancer receive neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.

Patients with complete lymph node response, partial lymph node response, or negative lymph node response were less likely to experience recurrence and increased survival in esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Circulating Tumor DNA as a Predictive Biomarker for Clinical Outcomes With Margetuximab and Pembrolizumab in Pretreated HER2-Positive Gastric/ Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma
Daniel V. T. Catenacci, MD, and colleagues present findings from a study of circulating tumor DNA as a predictive biomarker for gastric and gastroesophageal cancer.
Investigators report that patients with advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma may have superior overall survival benefit following treatment with tislelizumab/chemotherapy vs placebo/chemotherapy.

Long-term survival benefit is seen in patients with treatment-naïve advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma who were treated with nivolumab plus chemotherapy or ipilimumab.