New research has identified specific gene mutations that occur in precancerous esophageal lesions, a finding which was then put into use with a simple non-endoscopic test.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


New research has identified specific gene mutations that occur in precancerous esophageal lesions, a finding which was then put into use with a simple non-endoscopic test.

Rectal cancer management is becoming increasingly complex. There is increasing recognition of the potential to avoid routine chemoradiotherapy, as excellent results can be achieved with a more selective approach.

Although the current standard treatment for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer is preoperative chemoradiotherapy followed by total mesorectal excision, concerns have been raised over the functional sequelae and possible overtreatment of rectal cancer patients.

In this article, we review risks and benefits of the standard treatment approach for rectal cancer and compare standard treatment with alternative methods aimed at rectal preservation.

Colorectal cancer patients with higher levels of plasma vitamin D have better survival outcomes, according to a new prospective study.

Age is a prognostic factor for both overall survival and progression-free survival among patients diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer, according to the results of a study.

Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy did not improve resection rates or survival outcomes in patients with early-stage, locally advanced esophageal cancer.

A new study provides evidence that a daily aspirin may reduce the risk of developing pancreatic cancer.

Consuming more than two servings of fish each week can reduce a person’s risk for recurrence of colorectal cancer, according to the results of a cross-sectional multinational study.
Methods of screening for colorectal cancer are estimated to have prevented between a quarter of a million to a half a million colorectal cancers, according to a recently published study.
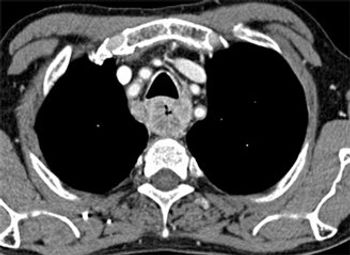
Preoperative staging of esophageal cancer with PET/MR is approximately as good as with endoscopic ultrasound, and may improve slightly over ultrasound and PET/CT scans, according to a new study.
Searching for and eradicating the bacteria Helicobacter pylori could reduce the incidence of gastric cancer in otherwise healthy individuals, especially in Asian populations, according to a new study.

Until anatomic staging and physiologic prediction models improve, induction therapy serves as a useful crutch that can mitigate the weaknesses in both of these important preoperative tasks.

Both esophageal cancer and stomach cancer are aggressive malignancies with contrasting risk factors, histologies, and molecular characteristics-yet for the most part comparable therapeutic approaches.

The purpose of this review is to update, present some of the new data on, and outline the controversies regarding neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy of esophagogastric junction and gastric adenocarcinoma.

Colorectal cancer screening should be considered in unscreened patients aged 75 years or older, especially those with no comorbid conditions, according to a new study.
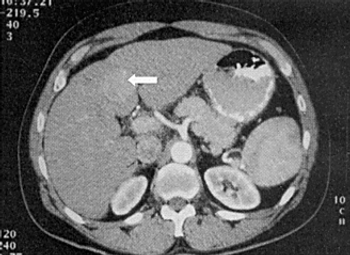
Treatment with sorafenib after curative resection or ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma did not improve recurrence-free survival compared with placebo, according to the results of the phase III STORM trial.

The addition of cediranib to treatment with cisplatin/gemcitabine did not improve progression-free survival in patients with advanced biliary tract cancer, according to the results of the phase II ABC-03 trial.
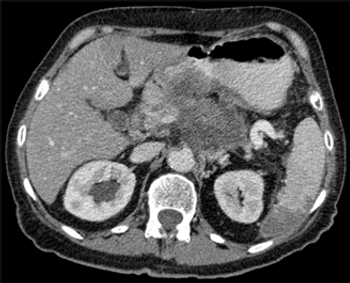
The JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib may improve overall survival in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer characterized by an elevated CRP, a well-established marker of inflammation.
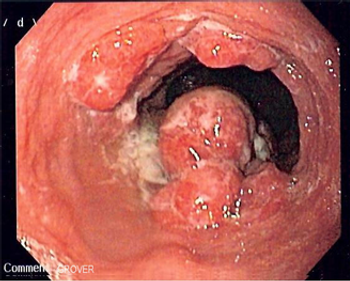
Adding ramucirumab to FOLFOX did not delay progression in patients with untreated advanced gastric or esophageal adenocarcinoma, according to trial results presented at the 2014 ASCO Annual Meeting.

First-line treatment with chemotherapy plus either bevacizumab or cetuximab resulted in equally effective outcomes for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.

The VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor apatinib significantly prolonged overall survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer compared with placebo, according to the results of a phase III study.

As part of our coverage of the ASCO Annual Meeting, we discuss advances in the management of upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract tumors, as well as highlighting clinical trial results that will be reported at the meeting.

As part of our coverage of the 2014 ASCO Annual Meeting, we discuss some of the colorectal cancer research that is expected to be presented at the meeting.
A blood-based test of four biomarkers including CA 19-9 may help clinicians diagnose pancreatic cancer at an earlier stage.