The use of adjuvant radiotherapy in patients with pT3 prostate cancer subsequent to radical prostatectomy is safe, according to 10-year follow-up results presented at the 2013 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The use of adjuvant radiotherapy in patients with pT3 prostate cancer subsequent to radical prostatectomy is safe, according to 10-year follow-up results presented at the 2013 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium.
In two phase III studies-READY and VENICE-targeted agents combined with standard first-line chemotherapy failed to increase overall survival for men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Physicians treating men with high-risk prostate cancer can safely reduce the duration of androgen blockade given in combination with pelvic radiation from 36 months to 18 months without compromising outcomes, including survival.
New data suggest that surveillance of patients with small kidney tumors may be a safe alternative to surgery, especially in older patients or those with comorbid conditions.

Ahead of the ASCO GU meeting, we spoke with two symposium committee members, Dr. Mack Roach, of the University of California, San Francisco, and Dr. Hans T. Chung, of the University of Toronto, about early treatment and surveillance of prostate cancer patients.
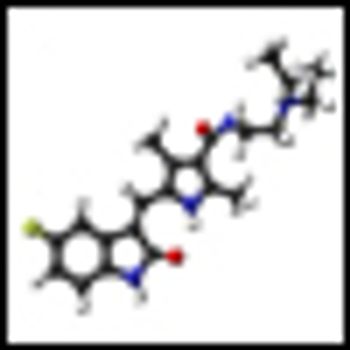
In a new study, researchers show that sunitinib, an FDA-approved TKI for advanced renal cell carcinoma, does not result in accelerated growth of kidney tumors after discontinuing treatment.
Localized prostate cancer treatment with surgery or radiation results in similar long-term side effects, such as erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence.
The mTOR inhibitor everolimus (Afinitor) has been found to significantly reduce the size of angiomyolipomas, the slow-growing benign tumors commonly associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) and sporadic lymphangioleiomyomatosis, according to the results of the phase III EXIST-2 study.
Researchers have identified bladder cancer markers that can predict which patients may have the most aggressive, fatal type of the disease. It was also discovered that smoking can affect the course of bladder cancer development, leading to more aggressive forms of the disease.

Focal therapy is an appealing addition to our current AS strategies. As a “lesser evil,” focal therapy is showing promise as a therapy that can provide cancer control, while also avoiding many of the radical treatment–associated morbidities.

The ideal utilization of focal therapy is to treat a smaller prostate cancer in which you can ablate, excise, or render inconsequential a tumor that affects a relatively small fraction of the gland.
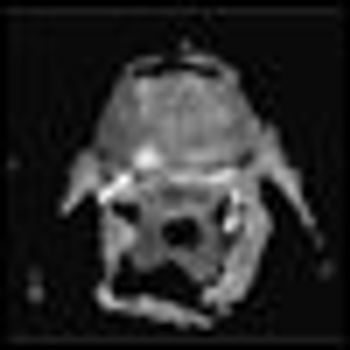
In this review we focus on the recent evolution of the concept of focal therapy and the potential applications of this management approach within an array of options currently available for patients with localized prostate cancer.
A new technique of robotic partial nephrectomy has the potential for better preservation of kidney function and better cancer control during partial nephrectomy by allowing surgeons more time to perform the procedure compared with traditional open surgery, according to the results of a recently published case series.
A new study shows that chemoprevention with anti-androgen therapies does not benefit all patients at risk for prostate cancer, and that in patients with a certain genetic mutation they can spur on more aggressive disease.

Recent progress in our understanding of the pathogenesis of advanced prostate cancer has heralded a new era in treatment. Numerous agents now populate the treatment landscape, and an impressive number of novel agents are in development. However, many questions remain unanswered, paving the path for discovery in the future.
This review summarizes recent findings in clinical prostate cancer research reported at the 2012 Annual Scientific Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) and addresses their relevance to clinical practice.
Screening patients with renal masses with iodine-124-girentuximab had both a high specificity and sensitivity for identifying clear cell renal cell carcinoma, according to the results of a newly published open-label multicenter study.
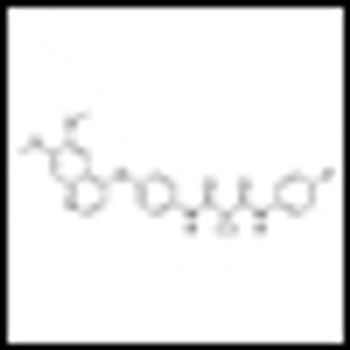
A phase II study indicates that cabozantinib has strong antitumor activity in advanced castration-resistant prostate cancer and improves bone scan lesions.

The expanded FDA approval of abiraterone acetate (Zytiga) now includes its use prior to chemotherapy in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
In mid-October, Pfizer announced that its phase III study being conducted examining axitinib (Inlyta) in treatment-naive patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma failed to meet its primary endpoint of improving progression-free survival compared with sorafenib.

Black patients diagnosed with renal cell carcinoma had worse survival than white patients regardless of several patient and tumor characteristics including tumor stage and size, according to data from 39,350 patients in the National Cancer Institute’s SEER program.

A phase I study of the use of stereotactic radiosurgery as a therapeutic option for patients with localized, inoperable primary renal cancer showed that the treatment modality effectively stabilized or decreased disease in a large percentage of patients.
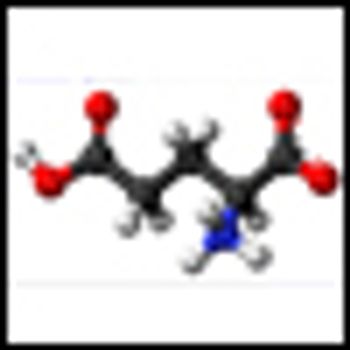
Researchers have identified a targetable metabolic pathway important for the growth of prostate cancer. The research may also have identified a potentially useful biomarker that can measure the aggressiveness of primary prostate tumors.
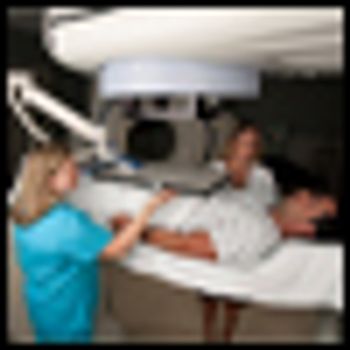
Radiotherapy directly after a prostatectomy in prostate cancer patients has long-term benefits, says a 10-year study. The study shows that radiation can prevent biochemical progression, as measured by rising prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels.

We describe areas where major inroads were initially achieved by targeting angiogenesis and by unraveling pathways in the heterogeneous tumors of mesenchymal origin-spurred by the identification of c-Kit–activating mutations in GIST and the regressions that ensued when tumors harboring these mutations were exposed to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (Gleevec).