
The majority of patients with systemic prostate cancer treated with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) will develop castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The majority of patients with systemic prostate cancer treated with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) will develop castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).
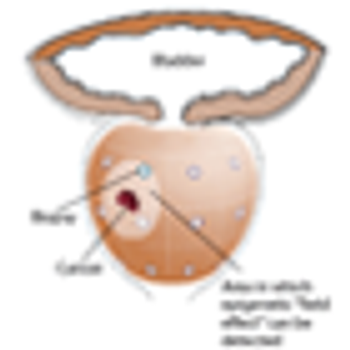
A 46-year-old man sought consultation for an abnormal prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level of 9 ng/mL and one prior negative biopsy. Five months ago, while traveling, he had presented to an urgent care facility with a 24-hour history of fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting.
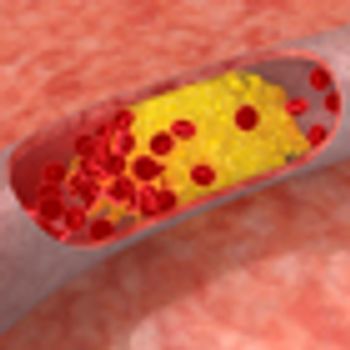
A cohort-based study found that men with prostate cancer who took cholesterol-lowering statins had a lower risk of dying from their prostate cancer.
A study found that robotic partial nephrectomy to remove kidney cancer tumors resulted in better outcomes, but also had significantly higher hospital charges. The data were presented at the annual meeting of the American Urological Association.

The FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee has voted 13 to 1 against AVEO's drug tivozanib for the treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
A case-control study of almost 500 men suggests that obese men who have had a benign prostate biopsy have a greater risk of prostate cancer in the future.
A mouse model of bone metastasis can be used to follow real-time response to therapeutics in preclinical development, such as cabozantinib, according to results presented in the poster session of the 2013 AACR annual meeting.
The use of zoledronic acid (Zometa) had no effect on the prevention of bone metastases in patients with high-risk prostate cancer, according to the first results of the Zometa European Study, or ZEUS, presented at the European Association of Urology 28th Annual Congress in Milan, Italy.

A new immunoassay that tests for the presence of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT), L-plastin (LCP1), and nonmetastatic cells 1 protein (NM23A) may be an effective method for the early detection of malignant kidney cancer.
Even those renal cell carcinomas (RCCs) that are smaller than 4 cm may put patients at risk for aggressive cancer, according to a new study presented at the 28th Annual European Association of Urology Congress in Milan, Italy.
Researchers have identified the enzyme PKCζ, which acts as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer and is part of a pathway that partly controls cell growth and metastasis.

The concept of multiparametric MRI comes at an important time in the history of prostate cancer screening. It is a method that provides anatomic information about the location, number, size, and risk of prostate cancers. It permits more accurate targeted biopsies that will improve the quality of tissue obtained, thereby reducing the rate of upstaging associated with random biopsies.

Multiparametric MRI is a promising tool for identifying cancer within the prostate. It has the potential to drastically change the way prostate cancer is staged and treated. However, work remains to make this technique reproducible and accessible to the community-based radiologist and urologist.

Only the possibility of increasing survival with better tumor localization and staging is probable with multiparametric MRI-and improved survival with MR imaging in prostate cancer has not been shown in a clinical trial or meta-analysis to date.
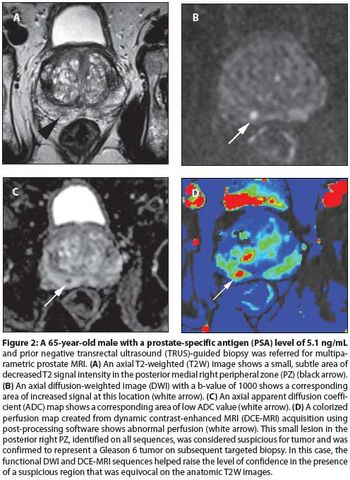
Our aims in this article are to describe the various imaging sequences that comprise the multiparametric MRI exam, as well as to review current literature on the strengths/weaknesses of these sequences; to delineate strategies for standardizing interpretation and reporting of MRI results; and to expound on the role of prostate MRI in clinical practice.

Targeting prostate cancer stem cells may be a method of treating prostate cancer while avoiding the development of resistance to androgen deprivation therapy, according to preclinical results presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Researchers have identified a mechanism by which prostate cancer resists hormonal therapy to develop into castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). The protein SIAH2 keeps a fraction of androgen receptors constitutively active in prostate cancer cells.
Imaging is important for both the diagnosis and management of prostate cancer. Standard techniques used in everyday clinical practice depend on the stage of the disease. Several new experimental modalities are currently in development to better identify and diagnose patients with progressive disease.

Radiolabeled small molecules targeting prostate-specific membrane antigen are well-tolerated tools for detection of metastatic prostate cancer, according to results of a phase I clinical trial.

This review focuses on targeted therapies related to these pathways of interest for the treatment of advanced urothelial carcinoma, describing the evidence to support further investigation of these approaches.

Current efforts utilizing genomic strategies to unravel the biology of urothelial carcinoma will undoubtedly lead to rational targets, new therapies, and a renewed enthusiasm among researchers and clinicians working in this field-which ultimately will improve the lives of patients with this devastating disease.

Acetaminophen and nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were associated with a 28% increased risk of developing kidney cancer, according to the results of a recently published meta-analysis.
Substitution of estrogen patches for luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist therapy in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer has similar testosterone-depleting effects while improving metabolic side effects, according to results from the PATCH trial.

High levels of physical activity were linked with a 22% decreased risk for renal cancer, according to a meta-analysis that looked at results from 19 studies that quantified the relationship with physical activity and renal cancer.
Men being treated for their prostate cancer with a gonadotropin-releasing hormone had a significantly increased risk for biliary disease compared with men who underwent no treatment, according to the results of a large, population-based study.