
This review discusses the rationale, history, and current status of proton therapy for prostate cancer-and controversies regarding it.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


This review discusses the rationale, history, and current status of proton therapy for prostate cancer-and controversies regarding it.

At the session on Management of Prostate Cancer in Older Adults: To Treat or not to Treat, Anthony D’Amico, William Dale, and Shabbir Alibhai all lent their clinical expertise in treating prostate cancer to outline the latest recommendations for screening and treating men for prostate cancer.
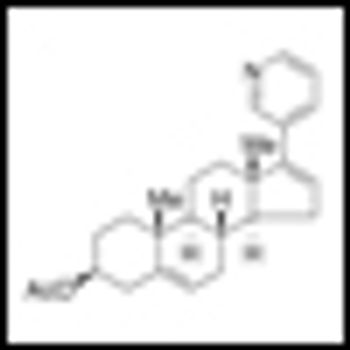
Abiraterone acetate has been shown to significantly acetate prolonged overall survival among patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) who previously received chemotherapy. The results of the Phase III study were published in the May 26, 2011 edition of the New England Journal of Medicine.
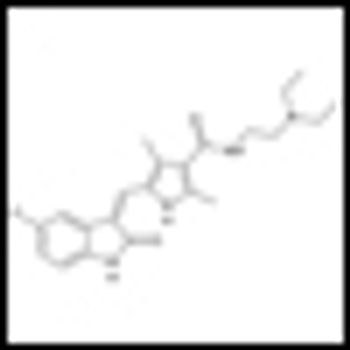
A retrospective study of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) patients published in the journal Cancer found that patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) had better overall survival and less-frequent metastasis to the brain.

Drs. Ruch and Hussain provide an excellent overview of the emerging therapeutic agents and targets for advanced prostate cancer.

The article by Ruch and Hussain provides a comprehensive overview of the progress that has been made in translating basic science findings in prostate cancer biology to clinical trials.

This article will present a detailed review of the body of evidence regarding the PSA assay, with reflections on the resulting future of prostate cancer screening.

This review will discuss recently FDA-approved agents for advanced prostate cancer and those under investigation in phase III trials.

Prostate cancer screening using prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing has been a contentious subject.

The controversy surrounding PSA screening is one of the most heated in oncology. The potential benefits include prevention of prostate cancer morbidity and mortality, but the men potentially harmed through overdiagnosis and overtreatment outnumber those who benefit.
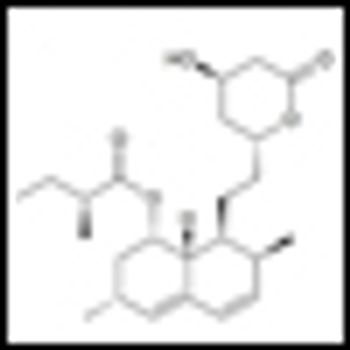
A large-scale, retrospective study published in the JNCI has now shown that men who take statins had lower incidence of total and high-grade prostate cancer compared with men who took antihypertensive medications.
Following a retrospective analysis which may be the largest of its kind to date, a multicenter team of investigators says treatment-related hypertension may be a useful biomarker of superior clinical outcome with sunitinib (Sutent) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC).

On April 28, the FDA announced the approval of abiraterone acetate (Zytiga) in conjunction with a steroid, prednisone, as treatment for late-stage (metastatic) castration-resistant prostate cancer patients who have received prior docetaxel.

My 2002 article provided an overview of the various interleukin-2 (IL-2)–based treatment regimens that had been explored over the preceding two decades
An analysis of data from 3,400 men in the large nationwide Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial indicates that, contrary to what might be expected, men with the highest blood percentages of DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), an omega-3 fatty acid commonly found in fatty fish, had 2.5 times the risk of developing aggressive, high-grade prostate cancer, compared with men who had the lowest levels.

The question of whether men with low-risk prostate cancer should have their cancers vigilantly monitored is an ongoing issue for the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Panel on prostate cancer.

As a clinician and researcher in the prostate cancer field, I have been hearing that prostate cancer is “20 years behind” breast cancer now for the last 25 years!

For many years, the results of large randomized clinical trials of cancer vaccines have not been good.
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of death in men in the United States; more than 217,730 new cases were expected to be diagnosed in 2010.[1] Although the majority of patients with advanced prostate cancer have an initial response to androgen deprivation, essentially all patients eventually progress to a castration-resistant state, manifested by rising levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA),

In a study reported in Nature online on February 2, researchers describe a four-gene signature that was more accurate than the standard Gleason score test in predicting which patients would die from metastatic spread of their prostate cancer.
The GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) drug Avodart (dutasteride), already approved for treatment in men with enlarged prostate glands, has been rejected by the FDA for the additional indication of reducing the risk of prostate cancer.

Adding chemotherapy to radiation therapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer may allow up to 67% of patients to be free of disease two years post-treatment, according to a study out of the UK. In addition, this treatment combination may offer a significant number of patients a better quality of life by avoiding surgery.

The article by Rove et al represents a comprehensive review of the recent clinical advances in the treatment of metastatic, castrate-refractory prostate cancer. The therapeutic armamentarium for the treatment of prostate cancer remains limited compared to other malignancies, such as breast cancer. It took approximately 14 years after mitoxantrone data emerged for us to see the approval of another chemotherapy agent, docetaxel. The successful outcome of recent clinical trials confirms that true advancement in prostate cancer treatment can be achieved by rational and rigorous clinical testing, but participation in prostate cancer clinical trials remains low, especially participation by African-American patients. Research study enrollment should be a high priority for those health care professionals who treat this disease.

Resistance to androgen deprivation is an ominous milestone in the natural history of metastatic prostate cancer:this disease state, now referred to as castration-refractory prostate cancer (CRPC), is historically associated with a median survival of less than two years. Until recently, only docetaxel (in combination with prednisone or estramustine) demonstrated a benefit in overall survival vs comparator therapy with mitoxantrone plus prednisone.[1,2] However, in the past year, compelling data in support of several promising new treatments for CRPC have been reported. The new data offer evidence-based treatment options, but also raise many questions for patient management and future clinical research.

Prostate cancer will be diagnosed in one of six men during their lifetimes, and a small portion of these will progress after primary and salvage therapies. For many years, there were few treatment options for these patients after routine hormonal maneuvers, and standard of care since the early 2000s has consisted primarily of docetaxel, which improved survival over the previous first-line therapy mitoxantrone. In recent years, however, new therapies have begun to emerge to treat this devastating form of prostate cancer. This review examines the mechanisms behind these therapeutics and the key trials seeking to validate their clinical use.