
Certain histologic variants of urothelial bladder cancer benefit more from neoadjuvant chemotherapy, according to a new study.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Certain histologic variants of urothelial bladder cancer benefit more from neoadjuvant chemotherapy, according to a new study.

Patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma had durable responses and manageable safety when treated with the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab.

In this interview we discuss the ASCO provisional clinical opinion on second-line hormonal therapy for chemotherapy-naive castration-resistant prostate cancer.

An immediate instillation of chemotherapy with mitomycin C following transurethral resection of a bladder tumor reduced the risk of recurrence of non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC).

Taller men are at increased risk for high-grade prostate cancer and prostate cancer death, according to a large registry study. Greater adiposity is also associated with higher-grade tumors and mortality.

Long-term follow-up found no significant differences in all-cause or disease-related mortality in men with early prostate cancer randomized to either radical prostatectomy or to observation. Surgery led to more adverse events, but less treatment for disease progression.

RNA splicing variants were found to be critical drivers of prostate cancer aggressiveness and therapeutic resistance in African American men.
A urine test of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) was found to be a reliable predictor of recurrence in non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer, according to a new study.

A phase II study has shown that savolitinib is active in a subgroup of patients with papillary renal cell carcinoma with gene amplification or mutations in the MET pathway.

Men with prostate cancer and one additional primary cancer may harbor a mutation in a cancer-predisposing gene, but the majority of these men do not meet criteria for clinical genetic testing.

After extended follow-up, the KEYNOTE-052 study has shown that first-line pembrolizumab offers durable responses and no new safety signals in patients with cisplatin-ineligible advanced urothelial cancer.

The combination of pembrolizumab and the IDO1 inhibitor epacadostat was active and generally well tolerated in patients with urothelial carcinoma.
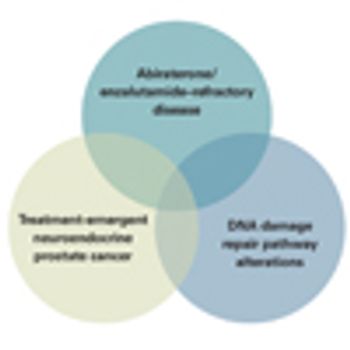
In this article, we look at both metastatic hormone-sensitive and metastatic castration-resistant disease, and we highlight several of the emerging categories of advanced prostate cancer that have direct implications for patient management.

Despite high rates of toxicity, a first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor/immunotherapy combination exhibits promising antitumor activity in metastatic renal cell carcinoma.

In this interview we discuss decision making in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma.

The FDA has granted approval to pembrolizumab (Keytruda) in the first- and second-line settings for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma.

A prospective phase III validation study found that AZGP1 has significant prognostic utility as a biomarker in localized prostate cancer.

A study may be able to identify which men with aggressive prostate cancer will benefit from androgen deprivation therapy.

Two new studies presented at the Annual Scientific Meeting of the American Urological Association offer an improved understanding of some genetic underpinnings of prostate cancer.

An interim analysis of the phase III IMvigor211 study found that atezolizumab did not meet its primary endpoint of improving overall survival over chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer.

The FDA has granted accelerated approval to avelumab (Bavencio) for treating locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma patients whose disease progressed following treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy.

The FDA has approved durvalumab (Imfinzi) for the treatment of patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma whose disease has progressed after treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy.

The use of nephron-sparing surgery to treat stage I renal tumors increased between 2009 to 2013 in Australia, showing increased compliance with international guidelines.

A subset of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma experienced a reduction in tumor size after undergoing postprogression treatment with nivolumab.

The FDA has expanded its approval of atezolizumab (Tecentriq) for the treatment of advanced bladder cancer to include the initial therapy of patients who are not eligible for cisplatin chemotherapy.