Results from a small study suggest that treatment with interferon alpha 2a could help chronic myeloid leukemia patients discontinue imatinib treatment.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Results from a small study suggest that treatment with interferon alpha 2a could help chronic myeloid leukemia patients discontinue imatinib treatment.
A small retrospective study of heavily pretreated patients with chronic myeloid leukemia found bosutinib to be a good option in the fourth-line setting.

Stem cell transplantation from an HLA-genoidentical sibling or an HLA-matched unrelated donor did not affect outcomes among high-risk pediatric ALL patients.
A single-arm, open-label trial in Australia found that selective early switching from imatinib to nilotinib is feasible and effective in patients with CML.

CML patients with high CIP2A levels treated with second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors have better outcomes than those treated with imatinib.
Results of a single-institution study found the risk for fracture among survivors of hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation increased by nearly eight times.

The next few years hold great promise, as new agents emerge and others consolidate their place on our shelves. We will be forced to rethink strategies and redefine management as a new era of immuno-oncology dawns.

Here we review monoclonal antibodies that have received FDA approval for the treatment of NHL and CLL in the last 5 years, as well as promising agents in development.
In a phase I trial, DT2219, the novel bispecific ligand-directed toxin, has shown activity against relapsed and refractory B-cell lymphoma and leukemia.
In patients with AML, post-therapy parameters including minimal residual disease and remission were found to be independent prognostic factors for outcomes.
Induction treatment for acute myeloid leukemia with amonafide L-malate/cytarabine failed to improve the rate of complete response over daunorubicin/cytarabine.
Researchers have identified patient factors linked with the discontinuation of ibrutinib therapy for reasons other than disease progression.

A new study finds that childhood cancer survivors are at risk for pituitary hormone deficiencies after radiotherapy treatment to the head.
In two phase II trials, the protein synthesis inhibitor omacetaxine offered long-term efficacy in some patients with chronic-phase and accelerated-phase CML.
Researchers have shown that axitinib could be repurposed as a treatment for CML patients resistant to standard TKIs through a certain molecular mechanism.

The FDA has expanded the approved use of ibrutinib (Imbruvica) to include patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Using genome-wide association studies, researchers have identified a germline variant that is associated with intolerance to mercaptopurine in pediatric ALL.

In a recent study of pediatric ALL, minimal residual disease was able to predict patients who were at increased risk for relapse post-allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
Socioeconomic factors are reducing the use of combined-modality treatment for early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma, despite its association with increased survival.

In its Annual Report on Progress Against Cancer, ASCO has declared that the transformation in the treatment of patients with CLL is the “advance of the year.”
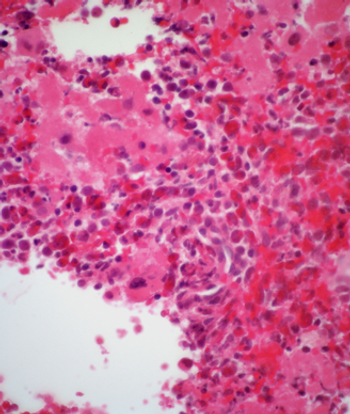
Long-term follow-up confirmed the previously reported result that intermittent administration of imatinib is safe and effective in CML patients.
Despite the early trial termination due to safety concerns, an analysis suggests that ponatinib offers improved efficacy over imatinib in newly diagnosed CML.

Clonal hematopoiesis with somatic mutations is strongly associated with the risk of developing blood cancers, according to a new study.
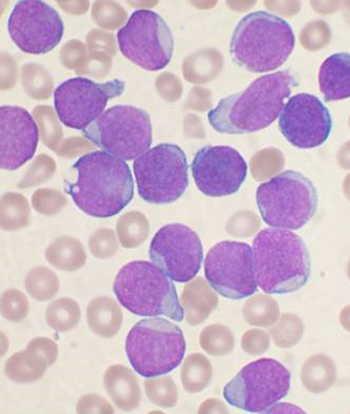
According to a report, two courses of the newly approved agent blinatumomab, for relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor ALL, will cost a staggering $178,000.

Autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation is a safe and effective treatment option for patients with HIV-associated lymphoma, according to a study presented at ASH 2014.