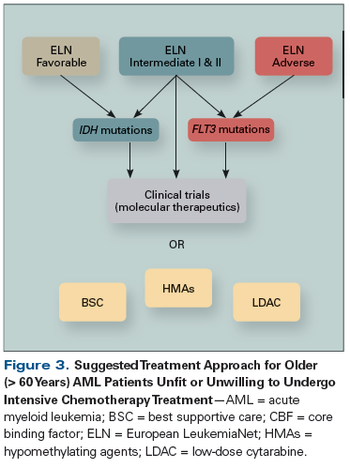
We review here the state of the art of diagnosis and treatment of AML and provide insights into the emerging novel biomarkers and therapeutic agents that are anticipated to be useful for the implementation of personalized medicine in AML.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


We review here the state of the art of diagnosis and treatment of AML and provide insights into the emerging novel biomarkers and therapeutic agents that are anticipated to be useful for the implementation of personalized medicine in AML.

Recent advances in mantle cell lymphoma include: (1) identification of new pathways to target, (2) novel therapeutics to treat patients with relapsed/refractory disease, and (3) monitoring of minimal residual disease and adoption of a maintenance therapy approach to prevent relapses post induction or post stem cell transplantation.

Significant variability in clinical target volume localization of gastric marginal zone lymphoma occurs if daily RT is delivered based on alignment to bony anatomy. MRI-guided RT allows for significant reduction in planning target volumes expansions without compromising coverage.

This analysis demonstrates that significant interfractional target variation exists in the treatment of GMZL; this variation could lead to difficulties in target localization and/or reproducibility of treatment. MRIgRT is a promising method to evaluate and allow for adaptation to these variations.

A rapid reduction in BCR-ABL transcript levels and the halving time of those levels are predictive of better outcomes in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia.

Overall, the future of patients with MCL is promising, since therapeutic options have widened. The implementation of universal aggressive treatment is challenged by novel regimens, targeted agents, the use of MRD to guide treatment decisions, and new trials that will directly compare transplant vs non-transplant approaches.

We are ready to move beyond a “one-size-fits-all” approach in AML and join our colleagues treating other malignancies, such as lung cancer, in moving towards a personalized medicine approach.

On April 11, 2016, The US Food and Drug Administration approved a new agent for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

A first-in-man phase I study of CUDC-907, which targets both histone deacetylase and PI3K enzymes, has shown promise in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma or lymphoma.

The long-term use of romidepsin in a dose-sparing regimen to treat cutaneous T-cell lymphoma may be a useful strategy to try to prolong disease response.

A significant number of children who have completed treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia may be experiencing anxiety or depression, according to a new study.

Patients with acute myeloid leukemia who have undergone autologous stem cell transplantation and survived without disease recurrence for at least 2 years are still at risk for late recurrences.

Patients with CML who are treated with dasatinib commonly experience lymphocytosis, and the condition is associated with higher response rates and increased survival in patients who are refractory or intolerant of imatinib.

The injectable drug APO866, designed to induce apoptosis, did not have efficacy against cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, according to the results of small study.

Elevated levels of TGF-α and IL-6 in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients were predictive of failure to achieve molecular response.

A study found an increased incidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, but no other secondary malignancies, in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with imatinib.

Temsirolimus produced some responses in patients with relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system lymphoma, but the responses tended to be short-lived.

Patients with chronic phase CML and pre-existing mild to moderate liver and/or renal dysfunction can be safely treated with frontline nilotinib or dasatinib, according to a new study.


Although a child’s socioeconomic status did not seem to significantly affect 5-year overall survival ALL, those children who were from high-poverty areas experienced early relapse compared with children who were from low-poverty areas.

Individuals with increased height or body mass index during adolescence showed an increased association with a diagnosis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

A phase I trial found that blinatumomab, a bispecific T-cell engager antibody, is feasible with regard to safety for treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

A new personalized DNA-based assay can detect very low levels of persistent disease in chronic myeloid leukemia patients thought to be in deep remission.

A number of clinical and sociodemographic factors, including age and gender, were found to be independently associated with fatigue and depression among cancer patients who were treated with hematopoietic cell transplantation.

Five-year results of the randomized phase III ENESTnd trial show a positive risk-benefit profile for nilotinib in patients with CML, as compared to imatinib.