
A full-term infant presents with abdominal distention and enlarged kidneys. After further evaluation, a biopsy is performed. What is your diagnosis?

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A full-term infant presents with abdominal distention and enlarged kidneys. After further evaluation, a biopsy is performed. What is your diagnosis?

A small study found that testosterone may suppress the growth of some advanced prostate cancers and could reverse resistance to testosterone-blocking agents.
Older men who received radiotherapy in addition to ADT had fewer deaths from their locally advanced prostate cancer compared with those treated with ADT alone.

While observation may be appropriate for select cases where prognosis is poor, rates of non-treatment are unacceptably high in muscle-invasive bladder cancer.

Extending the duration of androgen suppression in men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer prior to radiotherapy led to more adverse events and did not improve outcomes.
Long-term survival rates of patients after laparoscopic surgery for bladder cancer are similar to rates achieved with standard open surgery.

The purpose of this article is to present an updated set of American College of Radiology consensus guidelines formed from an expert panel on the appropriate use of radiation therapy in postprostatectomy prostate cancer.
A 63-year-old man with no family history of prostate cancer has prostate biopsy that revealed 9 out of 12 cores involved with prostatic adenocarcinoma, mostly Gleason score 5+4=9.

Molecular imaging in prostate cancer can play the additional critical role of an early biomarker for response to therapy, similar to how 18F-FDG is used in other malignancies.
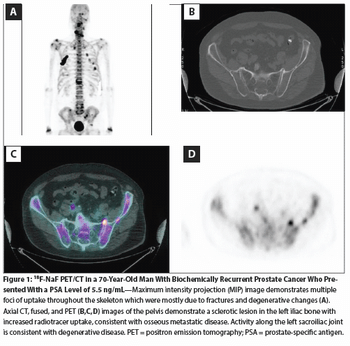
We briefly review these two imaging technologies and provide potential utilization strategies based on available data.

An extremely large database study across more than one million people found no increased risk of bladder cancer with the diabetes drug pioglitazone.
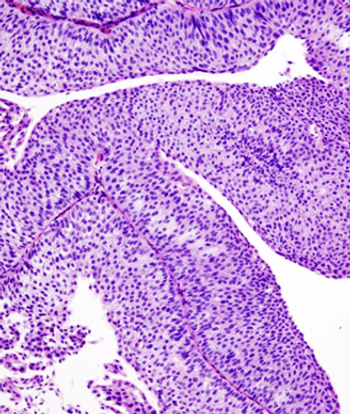
A large phase I study showed that the PD-L1 antibody known as MPDL3280A has promising activity in patients with urothelial bladder cancer.
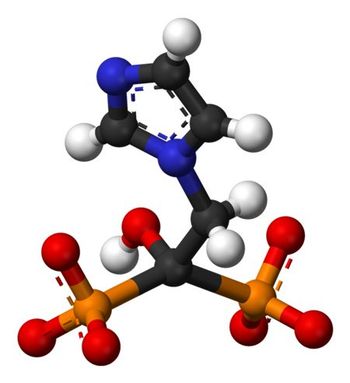
Despite recommendations calling for their use, prescriptions for bisphosphonates among older men with prostate cancer undergoing ADT are still low.
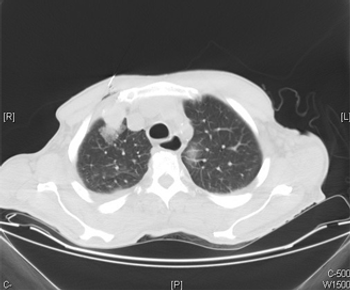
If physicians are following the current NCCN and AUA renal cell carcinoma surveillance guidelines, they could be missing as many as one-third of recurrences.

The use of a prostate cancer antigen 3 urine test could help men avoid undergoing unnecessary repeat biopsies, and predict which will be positive for cancer.

Clinical trial results to date show that men with visceral CRPC metastases do not benefit from ipilimumab, while their counterparts with bone- or node-only metastases do. This suggests that visceral metastases should be a stratification factor for future immunotherapy clinical trials.

While evidence points to benefit from highly active hormonal agents in prostate cancer with visceral involvement, the usefulness of immunotherapy is much less clear.
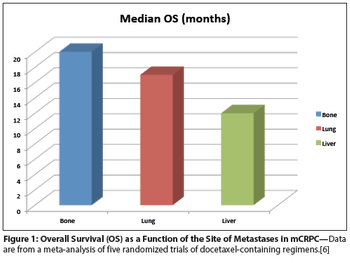
Although the mechanism(s) underlying the relatively poor prognosis of prostate cancer patients with visceral disease have yet to be fully elucidated, these new findings suggest that the microenvironment of bone lesions may be immunologically distinct from those at other sites.

One should not advise a patient with low- or very-low-risk prostate cancer to undergo a focal ablation. The kindest and gentlest approach is to first do no harm.

Investigators and physicians caring for the spectrum of prostate cancer should have a targeted treatment option available for patients who would benefit by it.
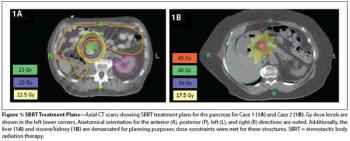
In this edition of our ongoing series, the authors present two cases involving renal cell carcinoma patients treated with SBRT for pancreatic metastases.
Participants from two separate studies with higher levels of vitamin B6 were found to have a lower risk for renal cell carcinoma.

An increased intake of lycopene may be associated with a decreased risk for renal cell carcinoma, according to data from a study of postmenopausal women.

Partial nephrectomy may be just as effective as radical nephrectomy for the surgical removal of clinical T2 renal masses, results of a new study indicate.

A study found that prostate cancer patients with a history of heart problems are at increased risk of cardiac death following androgen-deprivation therapy.