Frontline treatment with tebentafusp significantly improved overall survival in patients with metastatic uveal melanoma, according to data from the phase 3 IMCgp100-202 trial.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Positive Efficacy Data Found With Lifileucel TIL Therapy for Pretreated Advanced Melanoma

Frontline treatment with tebentafusp significantly improved overall survival in patients with metastatic uveal melanoma, according to data from the phase 3 IMCgp100-202 trial.
When compared against nivolumab alone, relatlimab plus nivolumab delayed progression in patients with unresectable stage III and IV untreated melanoma.

Adjuvant immunotherapy treatment was associated with a significant survival benefit for patients with stage II melanoma in a study presented at the Society of Surgical Oncology 2021 International Conference on Surgical Cancer Care.
First-line treatment with nivolumab plus ipilimumab showed a moderate improvement in overall survival and a manageable safety profile in patients with metastatic uveal melanoma.

The PD-1 inhibitor cemiplimab was granted approval in patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma previously treated with a hedgehog pathway inhibitor or for whom these therapies are not appropriate.

During the age of systemic immunotherapy, investigators observed a change in the incidence of second primary cancers after metastatic melanoma that included solid tumor and hematologic malignancies.

The novel viral immunotherapy PVSRIPO is designed to stimulate a patient’s innate and adaptive immune system to promote an antitumor response and establish long-term immunologic memory to help keep their cancer at bay.
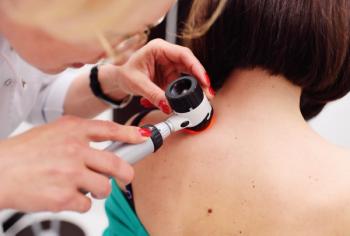
A study published in JAMA Dermatology found changes in diagnostics and awareness may, in part, account for initial increases in incidence rates for Merkel cell carcinoma.

The clinical trial of tebentafusp (IMCgp100) versus investigator’s choice in metastatic uveal melanoma met its pre-defined boundaries for statistical significance of the primary end point of overall survival in its first pre-planned interim analysis.

Study investigators indicated that these results call for the need to revise skin cancer health policies to be able to handle the increasing burden of keratinocyte carcinoma management.

Adil Daud, MD, spoke about the emergence of next-generation sequencing and the importance of testing patients with melanoma for BRAF mutations.

Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD, discusses the unmet needs professionals take into consideration when deciding treatment options for patients with melanoma.

Data from the COMBI-AD Trial evaluating dabrafenib and trametinib to treat melanoma was analyzed by Hussein Tawbi, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.

CancerNetwork spoke with Jason Luke, MD, FACP, at the SMR Conference regarding the latest updates on melanoma.

“The data reported, in addition to its ease of use, demonstrate the potential of [tavokinogene telseplasmid] in combination with pembrolizumab as a next-generation intratumoral IL-12 therapy that can induce regression of both locally treated and untreated distant and visceral lesions,” said Paolo A. Ascierto, MD.
Results from this study suggest that this combination is active and should be considered for this patient population, though additional research is still necessary.
Pretreatment circulating tumor DNA was found to be a reliable indicator of patient outcome for those with metastatic melanoma in the first-line immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) treatment setting, but not in the second-line setting.
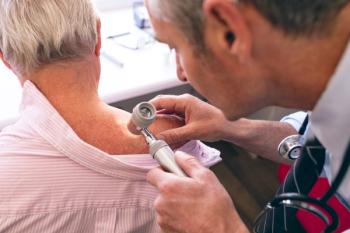
A study published in JAMA Dermatology determined that topical immunosuppressant medications used to treat adult patients with atopic dermatitis do not increase the risk of common forms of cancer despite warning labels on the packaging.

The study is evaluating the nivolumab-ipilimumab combination versus nivolumab alone in patients who have had a complete surgical removal of stage IIIb/c/d or stave IV melanoma.

Data for the phase 3 COMBI-i trial showed that spartalizumab combined with dabrafenib and trametinib did not meet its primary end xpoint of investigator-assessed progression-free survival.
Cemiplimab demonstrated an objective response rate of 31% in patients with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma who progress on or are intolerant to hedgehog inhibitors.
Partner Therapeutics, Inc. announced that its EA6141 study evaluating sargramostim in combination with ipilumimab and nivolumab to treat melanoma was approved to begin enrollment.
The study was evaluating spartalizumab in combination with dabrafenib and trametinib among untreated patients with stage IIIC or stage IV BRAFV600 mutation-positive cutaneous melanoma.
Data released from a phase 2b clinical trial showed statistically significant long-term survival for patients with stage III or IV melanoma at high-risk of recurrence.

The FDA approved atezolizumab plus cobimetinib and vemurafenib for the treatment of patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive advanced melanoma.