
While having an advance plan for end-of-life decisions has increased in cancer patients, aggressive treatments near the end of life continue to occur.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


While having an advance plan for end-of-life decisions has increased in cancer patients, aggressive treatments near the end of life continue to occur.

A new meta-analysis suggests that de-escalation of bone-targeted agents is a safe strategy in breast cancer patients with bone metastases.

Use of post-operative radiotherapy was associated with better overall survival in patients with incompletely resected stage II/III non-small-cell lung cancer.
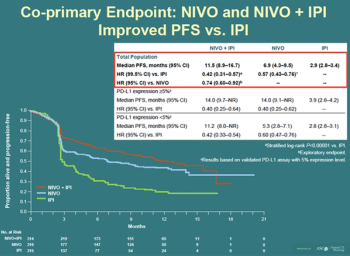
This slide show highlights some of the top studies and news on cancer to come out of the 2015 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, held in Chicago.

Some of the most brilliant physicians I have known have impressed me with their respect for colleagues. They would never express a difference of opinion by denigrating another practitioner, but recent experiences have opened my eyes to the arrogance of some physicians.

The presence of an abdominal blood clot may be a sign of cancer and may also be associated with poor survival for patients with pancreatic or liver cancers.
Using simulation modeling, researchers found that higher adenoma detection rates were linked with lower lifetime colorectal cancer incidence and mortality.

PSA-based screening for prostate cancer among men older than 50 has decreased since the 2012 USPSTF recommendations.

Here we discuss the efficacy and safety of zoledronic acid, denosumab, enzalutamide, abiraterone, and radium-223 and review the available data regarding the cost of denosumab compared with that of zoledronic acid.

Enhanced control of osseous metastases with both systemic life-extending therapies and bone-support medications has meaningful clinical impact for prostate cancer patients.

Without patients we have no mission to accomplish; whenever we lose someone to cancer our very identity as cancer fighters is threatened with extinction.

A study showed that prostate cancer patients with bone metastases could have a long-term response to ADT and an acceptable quality of life for 10 or more years.

Denosumab used as an adjuvant therapy in postmenopausal breast cancer patients on aromatase inhibitor therapy cut the risk of fractures in half.

Even in the absence of cranial radiation therapy, survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) have decreased neurocognitive function years later.

Men with prostate cancer assigned to intermittent ADT experienced more ischemic and thrombotic events than did men assigned to continuous ADT.

Most patients with advanced cancer, and up to 60% of patients with any stage of the disease, experience significant pain. The WHO estimates that 25% of all cancer patients die with unrelieved pain.

Many patients with advanced cancer undergo a wasting syndrome associated with cancer anorexia/cachexia and asthenia. In defining these terms a bit further, anorexia is associated with a marked loss of appetite and/or an aversion to food.

Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a clonal malignancy that results from expansion of the mature lymphocyte compartment. This expansion is a consequence of prolonged cell survival, despite a varied cell.

This management guide covers the risk factors, screening, diagnosis, staging, and treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

Although marked progress in controlling chemotherapy-induced emesis has occurred over the past 25 years, nausea and vomiting remain among the most distressing side effects of cancer chemotherapy.

This management guide covers the diagnosis and treatment of early-stage breast cancers, including lobular carincoma in situ (LCIS), ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), and both noninvasive and invasive disease.

This management guide covers the risk factors, symptoms, screening, diagnosis, prevention, and staging of breast cancer.

This chapter addresses the diagnosis and management of locally advanced, locally recurrent, and metastatic breast cancer, that is, stages III and IV disease.

This management guide covers the treatment of stage II breast cancer, malignancies with primary tumors > 2 cm that involve ipsilateral axillary lymph nodes and tumors ≤ 5 cm without nodal involvement.

Fatigue and dyspnea are two of the most common symptoms associated with advanced cancer. Fatigue is also commonly associated with cancer treatment and occurs in up to 90% of patients undergoing chemotherapy.

Results from a phase I/II study suggest that the immunotherapy nivolumab is safe and effective in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).

Aflatoxin, a naturally occurring toxin produced by certain types of molds, has been found to be associated with an increased risk of gallbladder cancer.

We present some tips and advice from the editorial board of ONCOLOGY on how to make the most at the 2015 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, including places to go in Chicago, nice spots at McCormick Place, and some recommended presentations and sessions.

A survey showed that cancer patients' attitudes about alternative medicines explained their use more so than demographics and clinical characteristics.