
This comprehensive guide for oncologists covers the diagnosis, staging, treatment, and management of esophageal cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


This comprehensive guide for oncologists covers the diagnosis, staging, treatment, and management of esophageal cancer.

This management guide covers the screening, diagnosis, staging, and treatment of cervical cancers.

Carcinoma of the epithelial lining (endometrium) of the uterine corpus is the most common female pelvic malignancy. Factors influencing its prominence are the declining incidence of cervical cancer, longer life expectancy, and earlier diagnosis.

Malignancies have been detected in approximately 40% of all patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) sometime during the course of their illness.
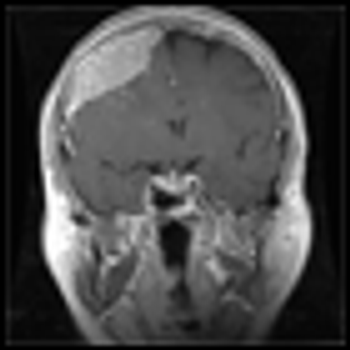
Intracranial neoplasms can arise from any of the structures or cell types present in the cranial vault, including the brain, meninges, pituitary gland, skull, and even residual embryonic tissue.

Carcinoma of an unknown primary site is a common clinical syndrome, accounting for approximately 3% of all oncologic diagnoses. Patients in this group are heterogeneous, having a wide variety of clinical presentations and pathologic findings.

Infections are among the most common, potentially serious complications of cancer and its treatment.

Malignant pleural effusion complicates the care of approximately 150,000 people in the United States each year.

This management guide covers the oncologic emergencies such as superior vena cava syndrome, deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and other paraneoplastic syndromes.

Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is the IV infusion of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells designed to establish marrow and immune function in patients with a variety of acquired and inherited malignant and nonmalignant disorders.

This management guide covers the symptoms, screening, diagnosis, and treatment of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), mesothelioma, and thymoma from a surgical, medical, and radiation oncology approach.


Skin cancer is the single most common form of cancer, accounting for more than 75% of all cancer diagnoses. More than 1 million cases of squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas are diagnosed annually, with a lifetime risk of more than one in five.

A treatment strategy including dose intensification with interval compression, use of the most active agents available, and the use of irinotecan as a radiation sensitizer led to a promising event-free survival rate in certain patients with metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma.

Oncologists, whether they like it or not, must develop some psychological skills if they ever hope to master the art of caring for people living with cancer.

In Hodgkin lymphoma survivors, both mean heart radiation dose and cumulative dose of anthracyclines significantly predicted cardiovascular disease.

The FDA announced the approval of trabectedin (Yondelis) for the treatment of liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma that is either unresectable or has metastasized.

Hypofractionated radiation therapy appears to lead to similar efficacy and safety as a standard radiation therapy regimen for men with low-risk prostate cancer.

Melanoma has historically been considered a radioresistant tumor. Emerging data have challenged this viewpoint. The potential roles of radiation therapy in the treatment of patients with melanoma will be reviewed here.

One of the more difficult topics to discuss concerning the ethics of healthcare is distributive justice-the fair distribution of benefits, risks, and costs.

Small intestinal “carcinoid” or well-differentiated grade 1 neuroendocrine tumors can have an insidious onset or be diagnosed serendipitously at the time of surgery, during the workup for another disorder, or during a screening test.

It is incumbent on melanoma and radiation oncology researchers alike to further our understanding of when and how RT can help patients.

A new study at a single center in Japan found no significant differences in the rate of BRCA mutations between ovarian cancer patients with or without family histories of the mutations and recommends that BRCA1/2 testing be required for all ovarian cancer patients

Palliative care should be provided with cancer care early in the course of illness for all patients with advanced disease, according to a new guidance statement from ASCO and the American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine.
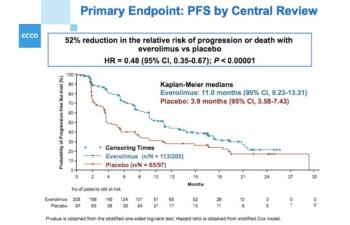
This slide show features some of the top highlights on neuroendocrine tumors, breast cancer, and renal cell carcinoma to come out of the 2015 European Cancer Congress in Vienna.

A simple one-question tool may help oncologists more accurately predict cancer patients’ prognoses and know when to initiate end-of-life discussions.

A novel program combining radiation oncology with palliative care in patients with painful bone metastases increased the use of proven treatments while maintaining pain management, decreased palliative radiation use, and decreased hospital length of stay.

The use of bone-seeking radionuclides effectively controlled bone pain in men with prostate cancer metastatic to the bone, according to the results of a systematic review.

Almost 40% of patients undergoing palliative radiotherapy to treat symptomatic bone metastases experienced pain flare, according to an observational study.
A new genetic analysis found five new genetic variants that raise the risk for gliomas. One of the five was associated with a sharply increased risk for glioblastoma.